Fig. 2.
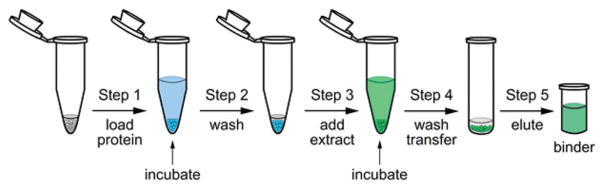
Functional chromatography arises through a 5-step procedure that can be completed in 6–12 h using conventional Eppendorf tubes and glass vials. (Step 1) The process begins by coupling a purified protein to a resin. Protein loading typically requires 1–2 h of incubation at 4 °C to complete. (Step 2) The protein-charged resin is capped to block reactive sites and washed to remove any unbound protein or blocking agent. (Step 3) A natural product extract is added in an aqueous buffer. (Step 4) After incubation, the resin is washed and transferred to a glass vial. The bound materials are eluted using 95% EtOH. Use of a glass vial at the elution stage was key to avoiding background from contaminants in plastic.
