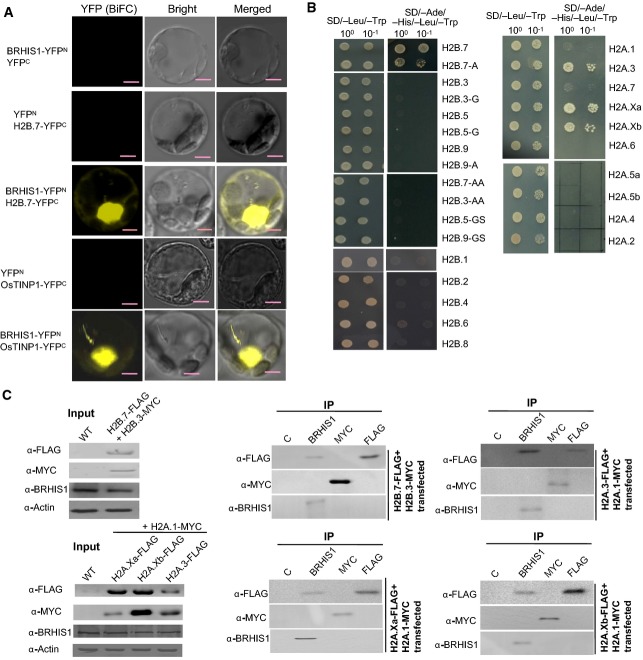
Figure 4.
BRHIS1 specifically interacts with OsTINP1 and certain histone H2A and H2B variants
- BiFC assays in rice mesophyll protoplasts confirmed the in vivo BRHIS1-H2B.7 and BRHIS1-OsTINP1 interactions. Scale bars, 5 μm. Representative images from three independent experiments are shown.
- Yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assays that tested the possible interactions between BRHIS1 and H2B (left panel) or H2A variants (right panel). 100 and 10−1 indicate the relative dilutions of yeast cells for Y2H. H2B.7-A, H2B.3-G, H2B.5-G, H2B.9-A, H2B.7-AA, H2B.3-AA, H2B.5-GS, and H2B.9-GS are mutants with mutations within the conserved H2B domain. Representative images from three independent experiments are shown.
- Co-IP analysis in rice mesophyll protoplasts transiently co-transfected with various constructs expressing FLAG- or MYC-tagged H2A and H2B variants. Immunoprecipitates of BRHIS1, FLAG, MYC, or normal control Rabbit IgG (C) were immunoblotted with anti-FLAG, anti-MYC, or anti-BRHIS1. The protein levels of BRHIS1 and FLAG-tagged- or MYC-tagged H2A or H2B variants in the transfected cells are also shown by Western blot analysis. 100 seedlings were pooled for each group. Representative images from two independent experiments are shown.