Fig. 5.1.
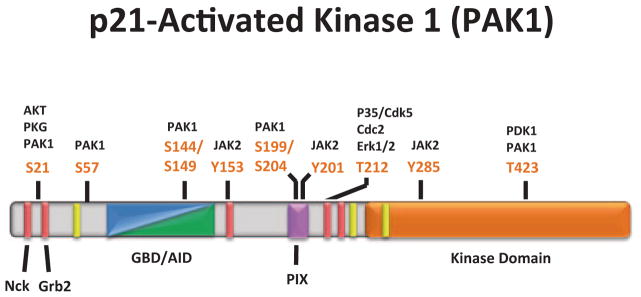
PAK1 domain structure and phosphorylation sites. The N-terminal regulatory region of PAK1 is composed of overlapping GBD/AID domains (aa 70-149, blue/green), five proline-rich regions (bright red), one nonclassical proline-rich region (aa 182–203, pink), and three nuclear localization signals (yellow). The C-terminal kinase domain (aa 249–545) is represented by the bright orange region. The two most N-terminal proline-rich regions (aa 12–18 and aa 40–47) mediate Nck/Grb2 binding, respectively, and subsequent PAK1 membrane localization. The non-classical proline-rich region regulates PIX/PAK1 binding and subsequent localization of PAK1 to adhesion complexes as well as facilitates PAK1 kinase activity. There are seven PAK1 autophosphorylation sites (S21, S57, S144, S149, S199, S204, and T423) that modulate PAK1 kinase activity, in addition to other sites phosphorylated by protein kinases that mediate PAK1 activity and localization. (Modified from Bokoch 2003)
