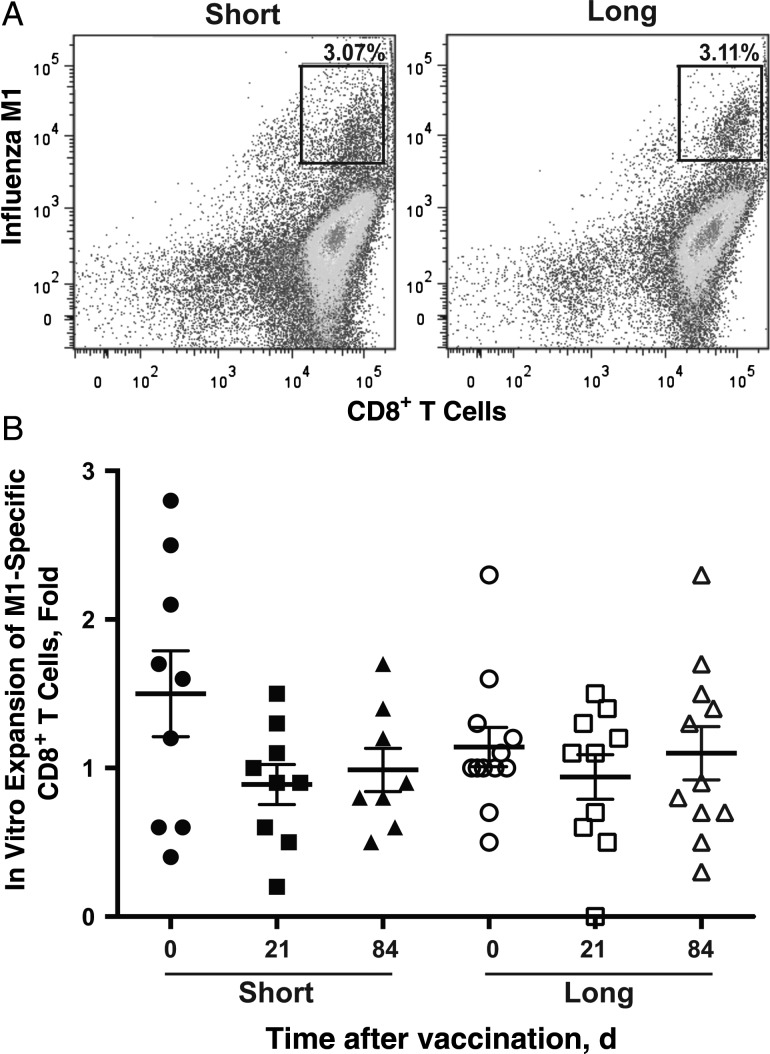
Figure 2.
No obvious differences were noted in antigen-presenting cell (APC) function between subjects in the short (n = 9) and long (n = 13) telomere groups. A, M1-specific CD8+ T cells after in vitro stimulation (% of total CD8 T cells). The differentiation of monocytes to APCs in vitro was described in “Participants, Materials, and Methods” section. Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting plots are presented for short and long telomere groups. B, Expansion of M1-specific CD8+ T cells after 7 days in vitro. Monocytes were isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells from each visit (day 0, 21, or 84 after vaccination, as indicated) of study subjects, cultured for 5 days in the presence of interleukin 4 (20 ng/mL) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (10 ng/mL), and then cultured for another day after lipopolysaccharide was added (100 ng/mL) at day 5. Mature APCs were pulsed with M158−66 (GILGFVFTL) (5 µg/mL), irradiated, and then incubated with CD8+ T cells from a healthy HLA-A2–positive adult for another 7 days. At the end of 7 days, cells were harvested for cell count, and M1-specific CD8+ T cells were analyzed with flow cytometry. Individual symbols represent values for individuals subject at a given visit (days 0, 21, and 84); means and standard errors of the mean are also shown.