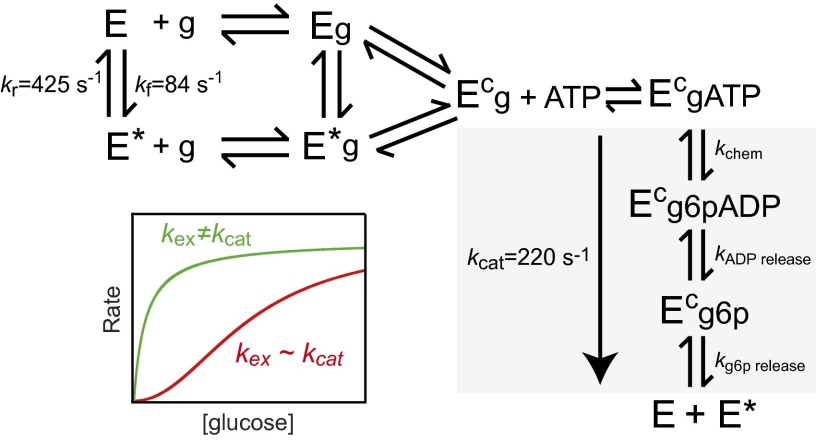
Fig. 4.
Model of GCK cooperativity. Unliganded GCK undergoes millisecond exchange between E and E* with a rate constant (kex = kf + kr) comparable to kcat, which produces kinetic cooperativity (red). Cooperativity is reduced (green) by alterations in kex or kcat such that these values are no longer comparable. α-type activation results from alterations in kex that cause a population shift toward one-state, whereas β-type activation results from alterations in kex and/or kcat that do not substantially perturb the conformational equilibrium. Steps that contribute to the value of kcat are colored gray, g is glucose, g6p is glucose 6-phosphate, and values for kex, kf, kr, and kcat are from ref. 36.