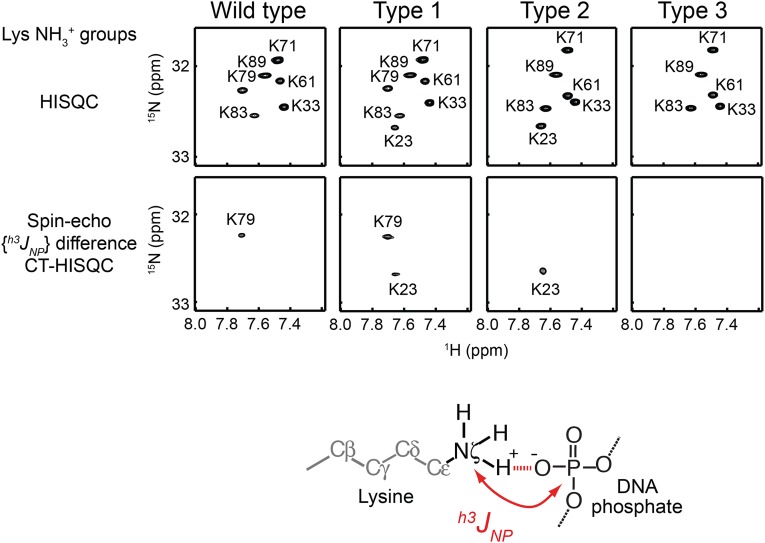
Fig. S1.
Engineering of intermolecular ion pairs between ZF and DNA as analyzed by 15N-31P scalar coupling h3JNP across a hydrogen bond. h3JNP data for the lysine side-chain NH3+ groups in the specific DNA complex of the Egr-1 ZF-DBDs were analyzed. The 1H-15N HISQC (63) and spin-echo h3JNP modulation difference constant-time HISQC (36) spectra for lysine NH3+ groups of each Egr-1 ZF-DBD bound to 12-bp target DNA are shown. The NH3+ resonances of this complex were assigned as previously (64). The spin-echo h3JNP modulation difference constant-time HISQC spectra show signals only for lysine NH3+ groups that form a hydrogen bond with DNA phosphate and exhibit sizable 15N-31P coupling across the hydrogen bond of the intermolecular ion pair (36). Because of the K79T mutation, the type 2 and type 3 mutant complexes do not show signals from K79. Because of the T23K mutation, type 1 and type 2 mutant complexes do show additional signals from K23. The presence of the h3JNP coupling for the K23 NH3+ group represents direct evidence of the intermolecular ion pair artificially introduced for the type 1 and type 2 mutant complexes (Fig. 1B).