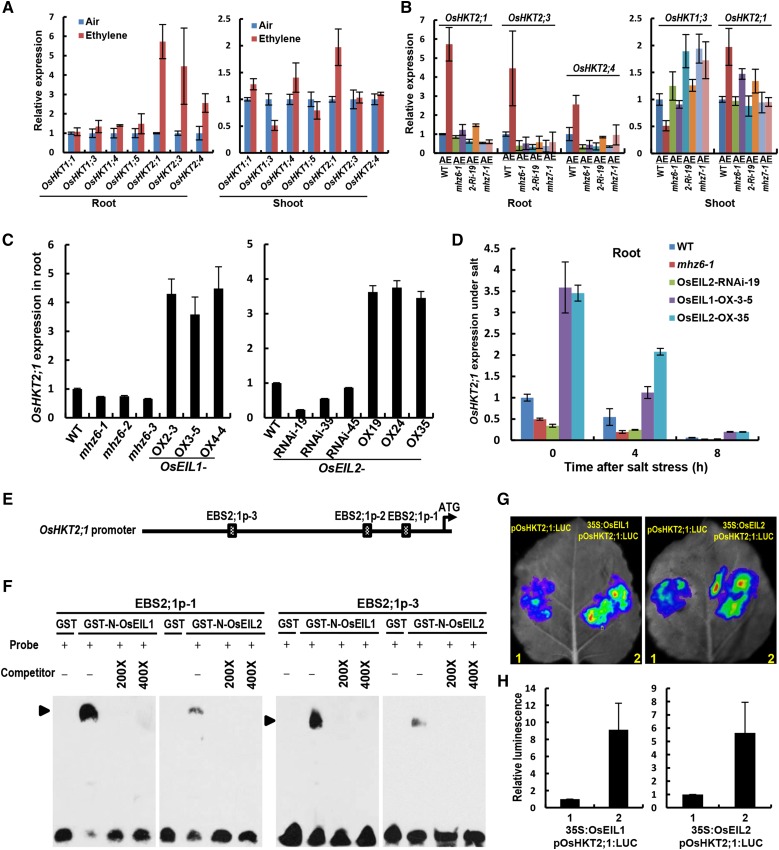
Figure 8.
MHZ6/OsEIL1 and OsEIL2 directly activate the expression of OsHKT2;1. A, Expression of OsHKT family genes in both shoot and root of the wild type. Light-grown seedlings were treated with or without 10 µL L−1 ethylene for 8 h. Values are means ± sd (n = 3). B, Expression of various OsHKTs in both shoot and root of wild-type (WT), mhz6-1, OsEIL2-RNAi-19 (2-Ri-19), and mhz7/osein2-1 plants. Details are as in A. C, Expression of OsHKT2;1 in roots of MHZ6/OsEIL1 and OsEIL2 mutation/RNAi and OX lines. Details are as in A. D, Expression of OsHKT2;1 in root of wild-type, mhz6-1, OsEIL2-RNAi-19, OsEIL1-OX-3-5, and OsEIL2-OX-35 plants under salt stress. Details are as in A. E, Schematic diagrams of putative EBS in the promoter of OsHKT2;1. F, MHZ6/OsEIL1 and OsEIL2 proteins bind to the EBS-containing region of OsHKT2;1. Glutathione S-transferase (GST)-tagged MHZ6/OsEIL1 and OsEIL2 N-terminal fusion proteins were incubated with biotin-labeled DNA fragments (Probe). Competition for the biotin-labeled promoter region was done by adding an excess of unlabeled wild-type probe (Competitor). Two biological replicates and two technical replicates were performed with similar results. G, MHZ6/OsEIL1 and OsEIL2 activated the promoter activity of OsHKT2;1 by transient expression in tobacco leaves. Five biological replicates were performed with similar results. H, Quantitative analysis of luminescence intensity for each comparison in G.