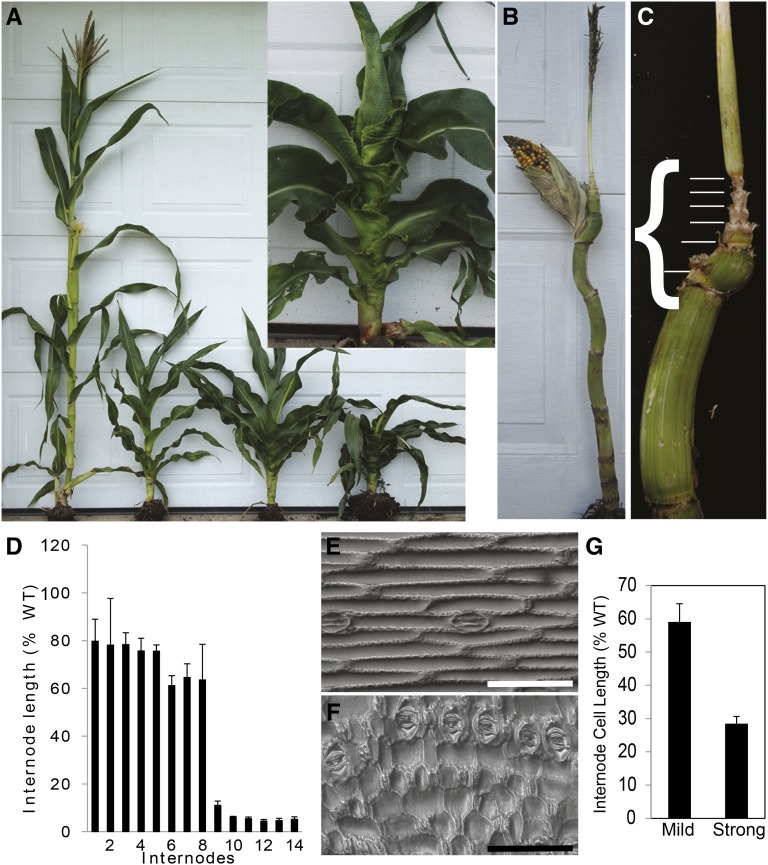
Figure 3.
zmbri1-RNAi plant architecture. A, zmbri1-RNAi plants with a wild-type (WT) sibling. The inset shows a closeup image of a zmbri1-RNAi plant. B and C, Dissected zmbri1-RNAi plants show extremely shortened internodes clustered between the ear and tassel nodes. D, Internode length measurements of zmbri1-RNAi plants. Bars show proportional internode lengths of the strong zmbri1-RNAi plants over wild-type siblings. While early internodes are moderately shortened, later internodes are strongly affected; the x axis represents internodes, and the y axis represents the proportional internode length of transgenic lines. E and F, Epidermal cells from internode 9 of the wild type (E) and zmbri1-RNAi (F). Bars = 100 μm. G, Internode 9 epidermal cells were shortened in both mild and strong zmbri1-RNAi lines. Bars show proportional cell length of zmbri1-RNAi plants over wild-type siblings.