Figure 3.
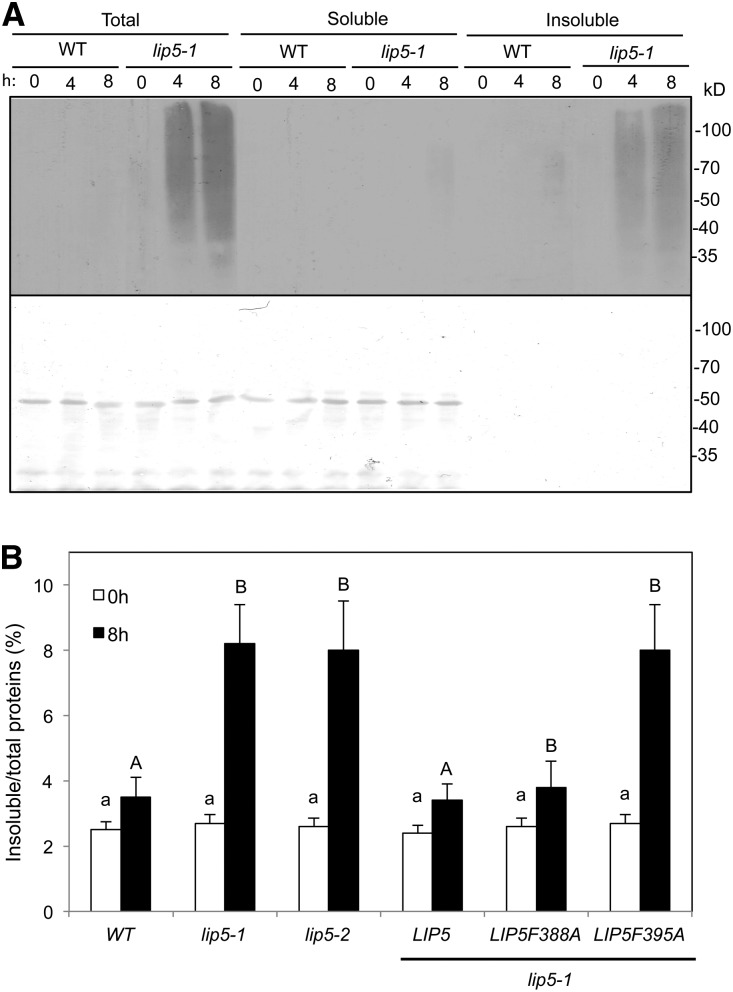
Increased accumulation of ubiquitinated aggregated proteins in the lip5 mutants under heat stress. A, Five-week-old wild-type (WT) and lip5-1 Arabidopsis plants were placed in a 45°C chamber, and leaf samples were collected at the indicated hours. Total proteins (Total) were extracted and separated into soluble and insoluble fractions by low-speed centrifugation. Soluble proteins in the supernatant (Soluble) and insoluble proteins in the pellets (Insoluble) isolated from equal amounts of total proteins for each sample were separated on SDS-PAGE gels, and ubiquitinated proteins were detected using western blotting with an anti-ubiquitin monoclonal antibody (top). Ponceau staining of the membrane blot before antibody probing is also shown (bottom). B, Accumulation of insoluble proteins. Leaf tissues from the wild type, lip5 mutants, and transgenic lines were collected at the indicated hours under 45°C for the preparation of total, soluble, and insoluble proteins. Total proteins in the starting homogenates and insoluble proteins in the last pellets were determined to calculate the percentages of insoluble proteins. According to Duncan’s multiple range test (P = 0.05), means do not differ significantly if they are indicated with the same letter.