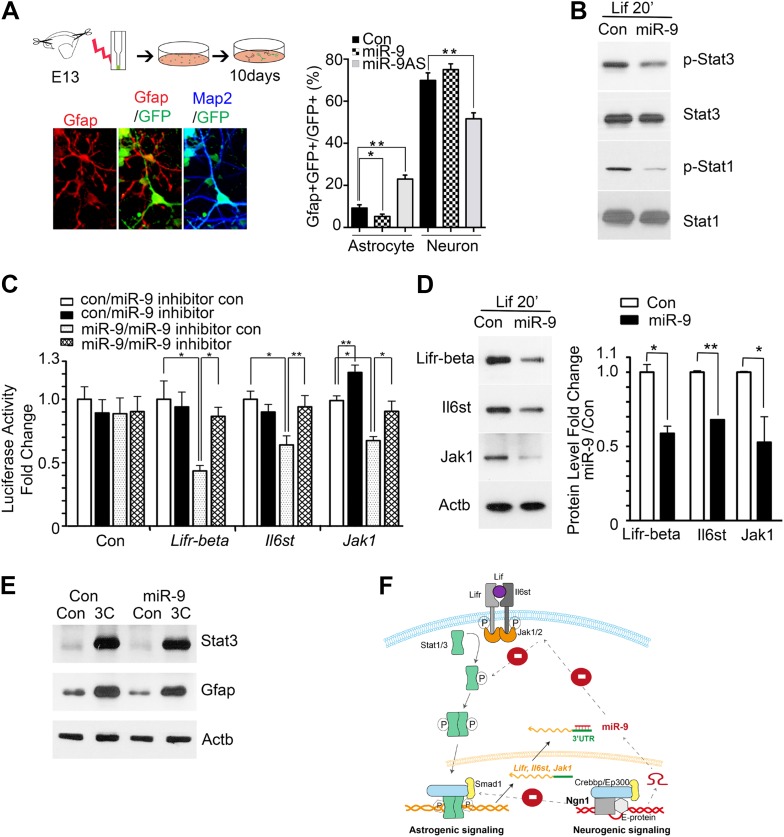
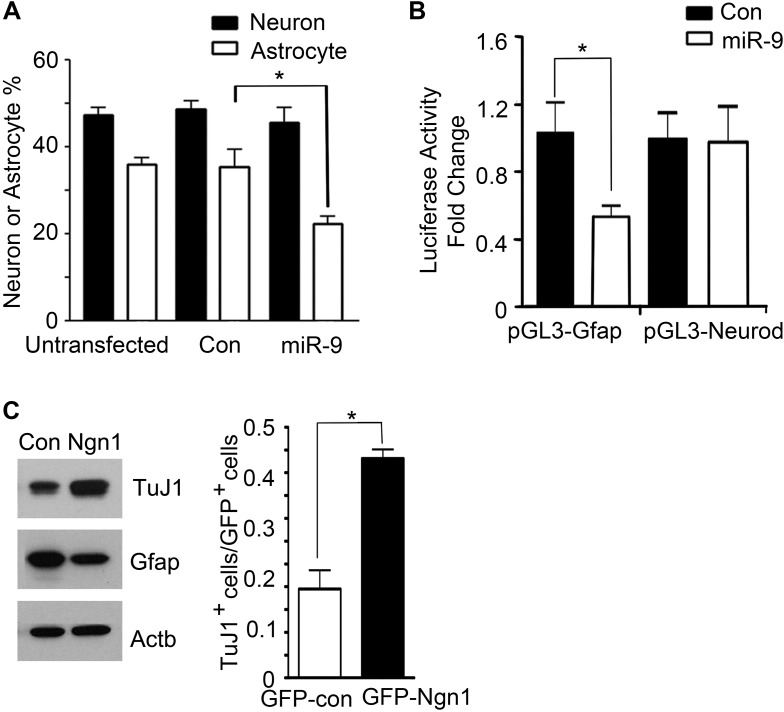
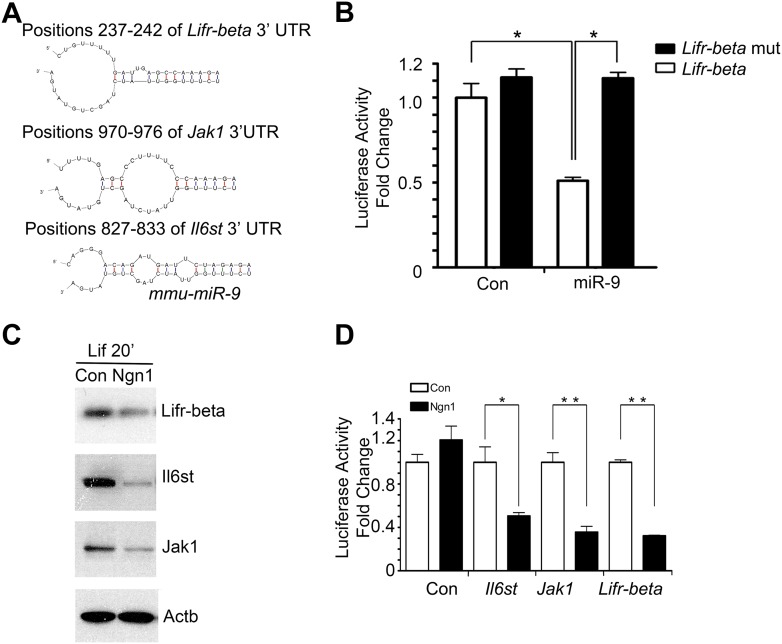
Figure 3. miR-9 inhibited astrogliogenesis via targeting three components of Jak-Stat pathway.
(A) Upper right panels: schematic representation of in vitro delivery of miR-9 constructs into cortical progenitors by electroporation. Lower left panels showed examples of astrocyte marker Gfap+ or neuronal marker Map2+ cells. Right panel showed overexpression of miR-9 significantly reduced the number of astrocytes 10 days after electroporation, whereas knockdown of miR-9 dramatically promoted astrogliogenesis (**p < 0.01, *p < 0.5, Mann–Whitney test). Overexpression of miR-9 in NPCs did not increase the number of neurons. Knockdown of miR-9 reduced the number of Map2+ neurons. Map2, Microtubule-Associated Protein 2. (B) Transfection of mouse NPCs with exogenous miR-9 duplex blocked phosphorylation of Stat1/3 without altering their protein levels. (C) Luciferase activity of Lifr-beta, Il6st (gp130), and Jak1 3′ UTR luciferase reporter in the presence of different combinations of control (con), miR-9, miR-9 inhibitor con, and miR-9 inhibitor in mouse NPCs. (D) miR-9 inhibited protein levels of Jak-Stat signaling components in NPCs transfected with control or miR-9 duplex. Right panels: western blotting densitometry analysis of protein level changes. Actb (β-actin) serves as the loading control. (E) A constitutively active form of Stat3, Stat3C bypassed the effect of miR-9 inhibition on astrocyte differentiation. (F) Schematic representation of Ngn1-regulated miR-9 signaling that modulates Stat1/3 phosphorylation to control cell fate specification. Ngn1 up-regulates miR-9 expression during neurogenesis. miR-9 reduces protein levels of Lifr-beta, Il6st, and Jak1 of Jak-Stat signaling pathway by targeting their 3′ UTRs, which in turn abolish Stat1/3 phosphorylation to suppress astrogliogenesis. Crebbp: CREB binding protein, Smad1: Mothers Against DPP Homolog 1 (Drosophila), Ep300: E1A Binding Protein p300, E-protein: ubiquitous basic-Helix-Loop-Helix proteins, such as E12 or E47. The dotted arrows show the inhibition regulations.