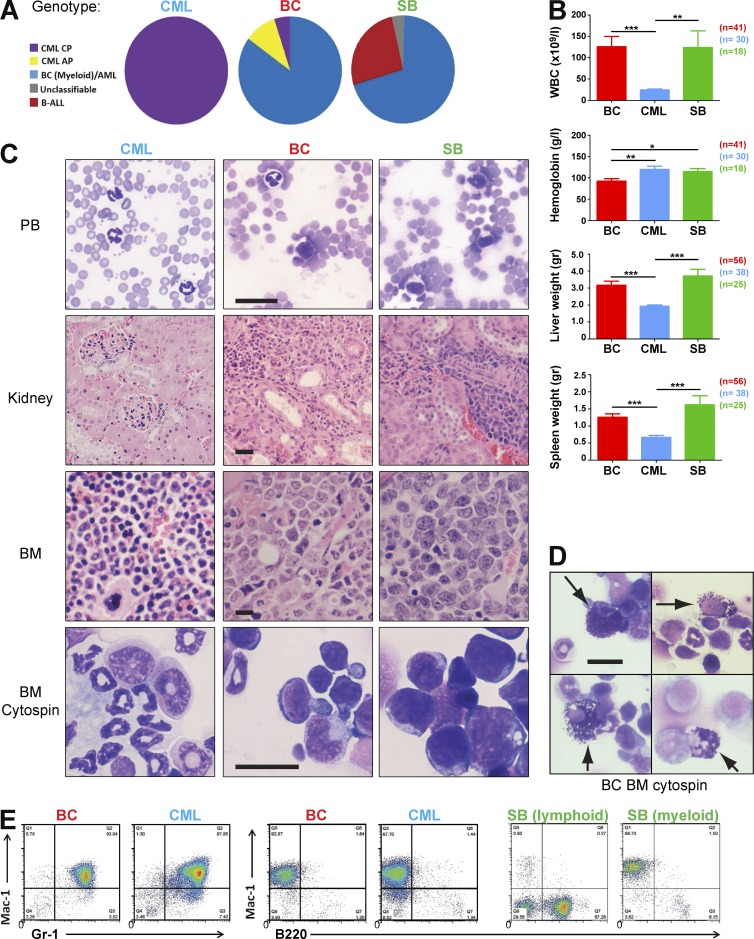
Figure 3.
Transposition leads to myeloid blast crisis. (A) Classification of all leukemias in each experimental cohort by the Bethesda criteria revealed a continuum of myeloid progression in the BC cohort with 85% demonstrating a myeloid transformation. In the SB cohort, 26% of cases were of a lymphoid phenotype. All mice in the CML cohort remained in the chronic phase of the disease. (B) Analysis of WBC, hemoglobin levels, and spleen and liver weights at the terminal endpoints between BC, CML, and SB mice (BC, n = 41; CML, n = 30; and SB, n = 18 for WBC and hemoglobin plots; BC, n = 56; CML, n = 38; and SB, n = 25 for liver and spleen weight plots). Student’s t test was used. (C) Peripheral blood (PB) smears, kidney, and BM histology sections and BM cytospins of representative CML, BC, and SB cases. (D) Cytospin preparations of BC BM from 4 cases showing characteristic abnormal basophils (arrowed), a feature often seen in human BC. (E) Representative flow cytometry profiles of CML, BC, and SB leukemias. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data are mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.0001. Bar, 25 µm.