Figure 1.
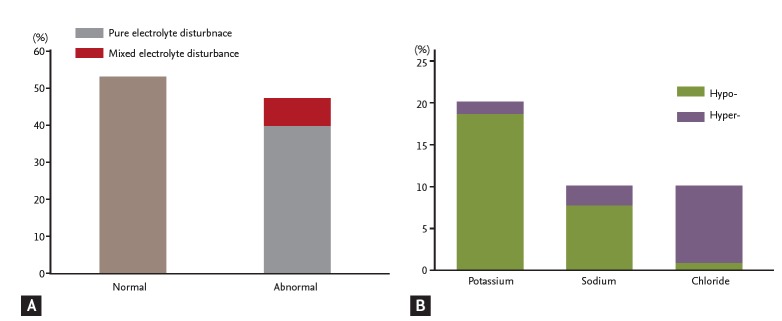
(A) The incidence of normal and abnormal blood electrolytes during severe hypoglycemia. (B) In pure electrolyte disturbances, the incidence of each electrolyte disturbance. The normal ranges for each electrolyte are defined as follows: sodium 135 to 148 mmol/L, chloride 95 to 110 mmol/L, potassium 3.5 to 5.3 mmol/L. Levels below the normal range are defined as hypoand levels above the normal range are defined as hyper-. A pure electrolyte disturbance was defined as an abnormal level in the one electrolyte and a mixed electrolyte disturbance was defined as two or three electrolyte levels being abnormal.
