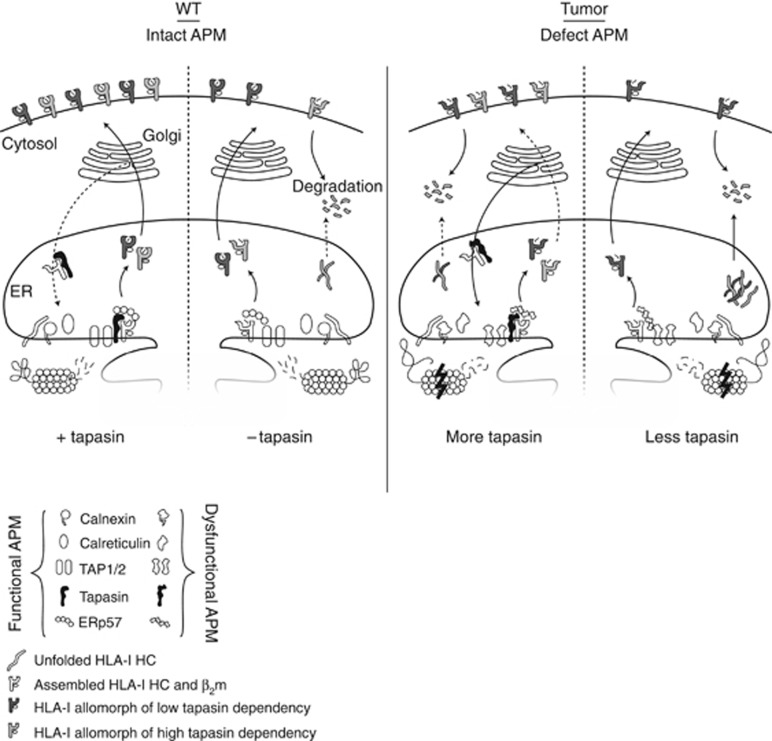
Figure 6.
Schematic figure of the effects of tapasin deficiencies and APM defects. The HLA-I and tapasin-deficient 721.220 cell line is often used as a model where an HLA-I allele of interest and tapasin is transfected into the cells to study the effect of tapasin on HLA-I surface expression. In these transfectants, the machinery of antigen processing is functional and the effect of tapasin is correlated with the surface expression of HLA-I, especially for HLA-I allomorphs with high tapasin dependency. In tumours, the APM is defect and thus the folding and maturation of HLA-I molecules are impaired even in the presence of tapasin. Tapasin can rescue misfolded HLA-I HCs from degradation through its retention/recycling function, but owing to defects in other parts of the APM many HLA-I molecules cannot reach a conformation making them stable enough to reach and efficiently present peptide on the cell surface. If there are multiple APM deficiencies including the level of tapasin expression, the maturation of HLA-I HCs are less successful, more HC is degraded and a higher proportion of unstable HLA-I molecules reach the cell surface.