Fig. 6.
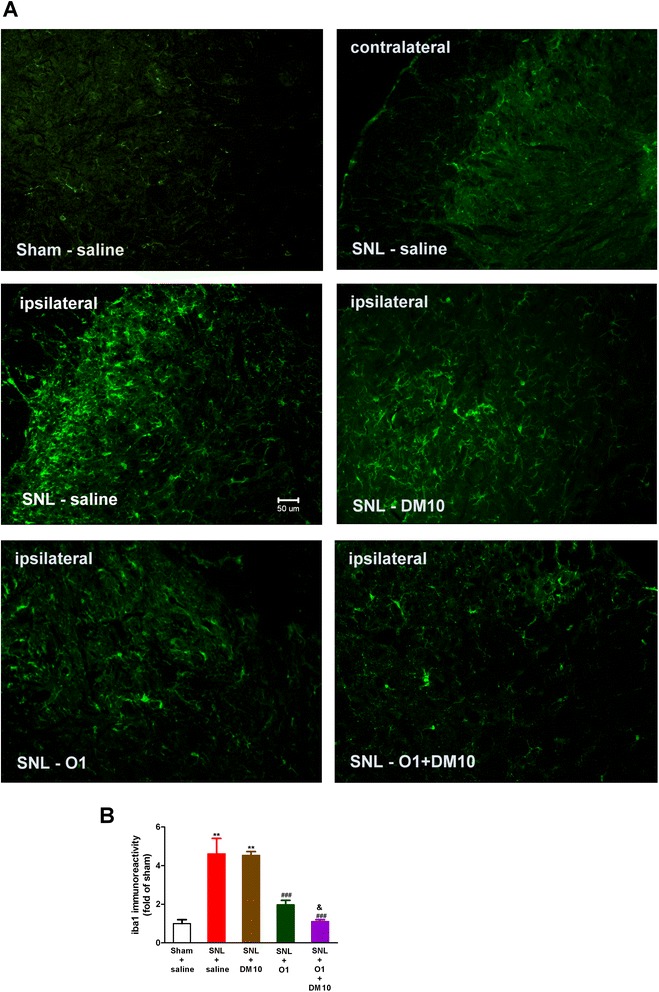
Co-administration of DM (10 mg/kg, i.p.) and oxycodone (1 mg/kg, s.c.) enhanced the effect of oxycodone to suppress SNL-induced activation of microglia in the L5 spinal cord dorsal horn. (a) Representative immunofluorescent images of microglia stained with iba1 (green; marker for activated microglia) on day 14 is shown for the following groups: Sham (ipsilateral), SNL (contralateral), SNL (ipsilateral), SNL-DM10 (DM 10 mg/kg, i.p.; ipsilateral), SNL-O1 (oxycodone 1 mg/kg, s.c.; ipsilateral), and SNL-O1 + DM10 (co-administration of oxycodone and DM; ipsilateral) (magnification: 20X). Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) Quantification of iba1-immunoreactivity after normalization for each group compared with control group (Sham + saline) on day 14. Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. (n ≥ 5). One-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls test were used to analyze the data. * P < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. Sham + saline group; # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001 vs. SNL + saline group; & p < 0.05 vs. SNL + O1 group
