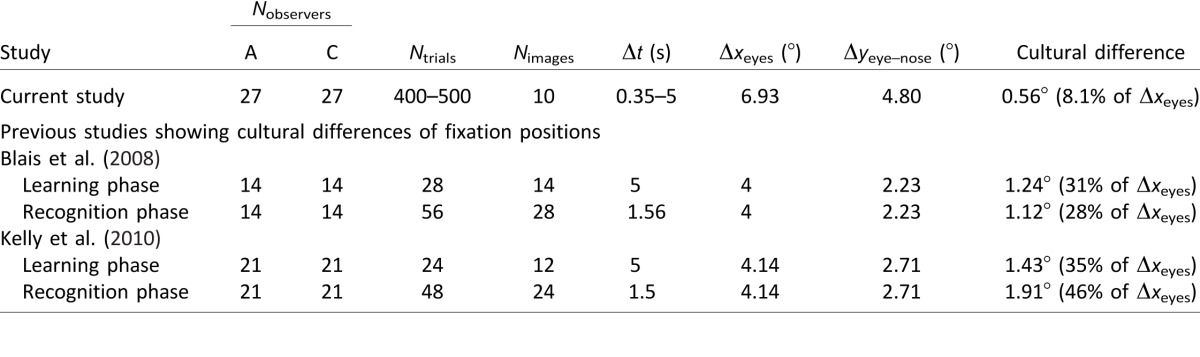
Table 11.
Cross-study comparisons of fixation differences across observer cultures. The cultural difference in the current study is the cross-cultural horizontal difference of the mean first fixation positions considering all observers in Experiments 1, 2, and 4 (see text). For previous studies (all using the learning-and-recognition tasks), the cultural difference is estimated by the vertical difference of the positions with the most positive and the most negative fixation biases (which happened to be at the eyes and the nose regions, respectively) in the difference iMap (Caucasian iMap − Asian iMap) considering all fixations (Blais et al., 2008, figure 2; Kelly et al., 2010, figure 2). Notes: Nobservers: number of observers. A: Asian observers. C: Caucasian observers. Ntrials: number of trials per face race. Nimages: number of images per face race. Δxeyes: mean interocular distance of faces. Δyeye–nose: mean eye–nose distance of faces.