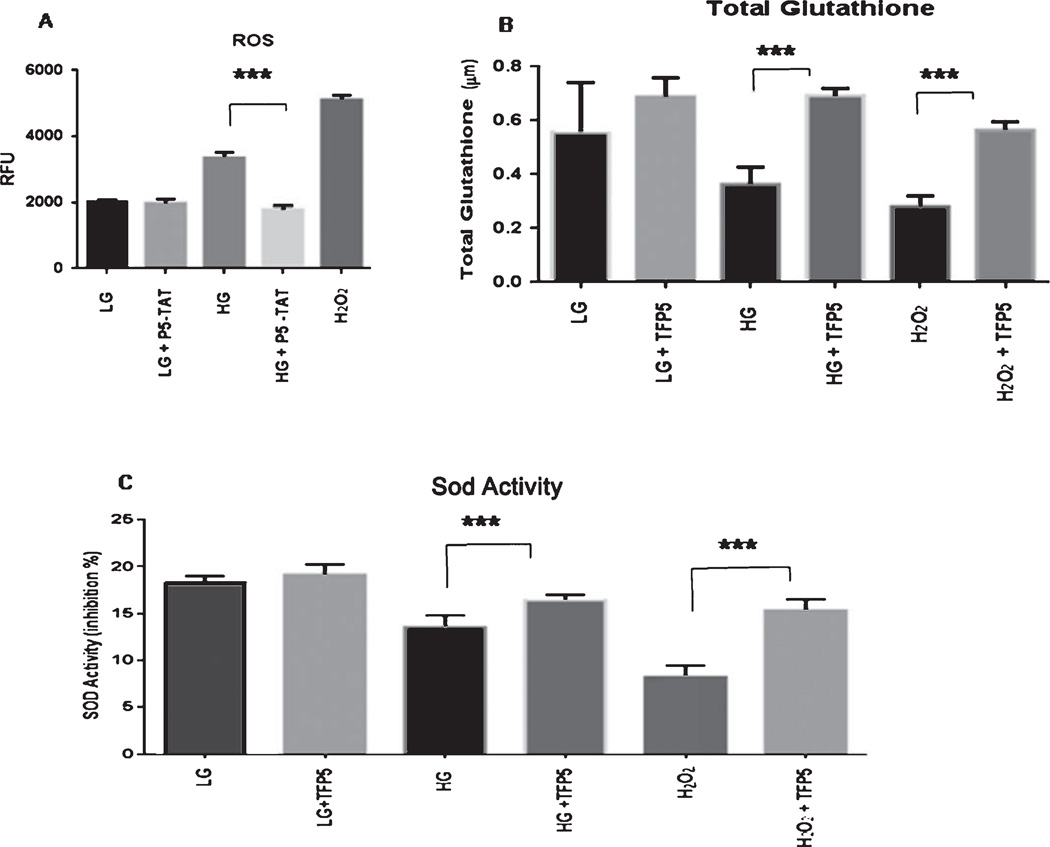
Fig. 3.
Pre-treatment with TFP5 rescues glucotoxic cortical neurons from oxidative stress due to increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and decreased antioxidant capacity. A). Cortical neurons were pretreated with p5-TAT (instead of fluorescent TFP5) for 12 h then incubated with DCFH-DA in the presence of different concentrations of glucose in culture medium for 8 h. DCF fluorescence was measured at 480 nm/530 nm using an OxiSelect™ assay kit for ROS. The results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of four independent experiments, ***p < 0.001. B, C) Primary cortical neurons were pretreated with/without TFP5 for 12 h then exposed to low (LG) and high glucose (HG) for 8 h before assaying for total glutathione and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity measured using an OxiSelect™ assays kit. H2O2 used as positive control. The results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of four independent experiments (***p < 0.001).