Figure 6. LPS modifications mediated by PhoPQ impact in vivo infection outcomes.
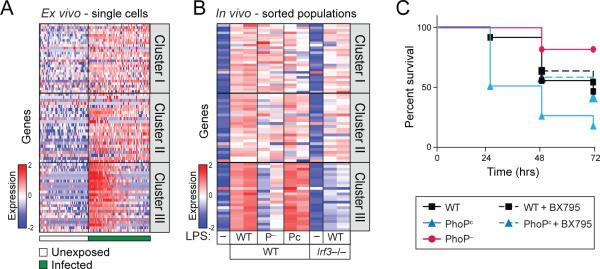
(A) Peritoneal macrophages, when infected ex vivo with GFP-labeled S. typhimurium show bimodal induction of Cluster III, like BMMs. (Table S6A) (B) Activation of the Type I IFN response in vivo was enhanced after stimulation with LPS extracted from PhoPc and reduced after stimulation with LPS extracted from PhoP– strain, compared to LPS extracted from WT S. typhimurium. As a control, no induction of the Type I IFN response was measured in Irf3−/− mice. (Table S6B) (C) Mice challenged with LPS extracted from PhoPc (blue, n=12) showed reduced survival compared to mice challenged with WT LPS (black, n=11). Inhibition of the Type I IFN response by co-administration of BX795 improved survival from PhoPc challenge, restoring it to WT levels (dotted blue, n=12). Mice challenged with LPS extracted from PhoP– (red, n=11) showed enhanced survival compared to WT.
