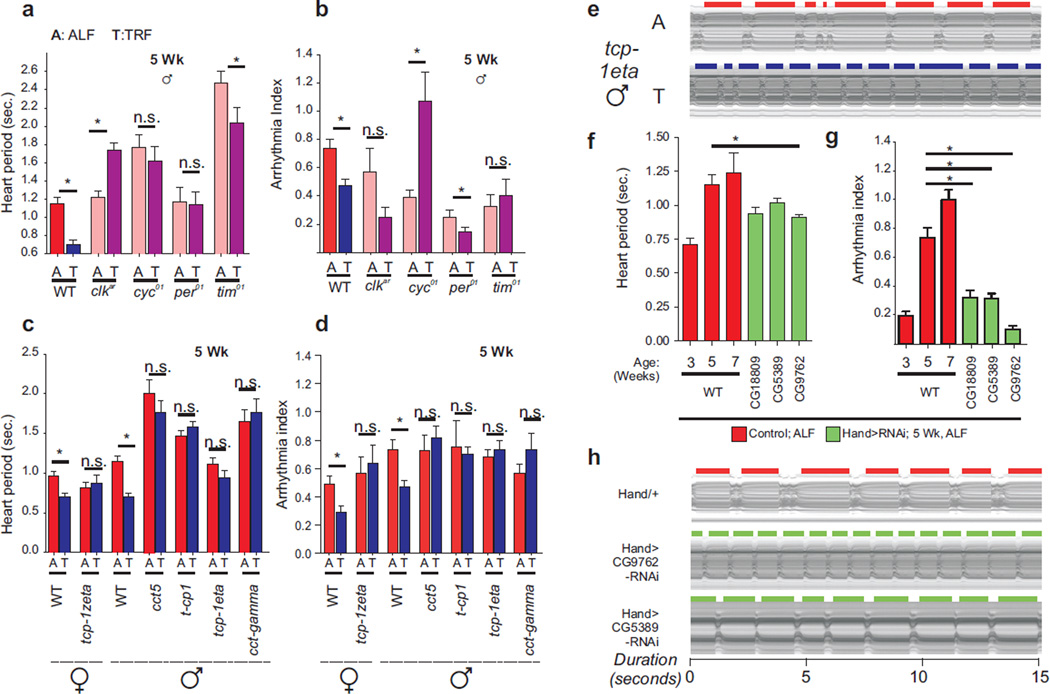
Fig. 4. Genetic basis for the beneficial effects of TRF.
5 week old flies carrying loss of function mutations in (a,b) clock components or heterozygous for P-element insertions in (c,d) TRiC chaperonin components fail to improve (a,c) heart period and (b,d) fractional shortening under TRF (n ≥12 circadian mutants, n≥17 TRiC mutants). Wildtype (Oregon-R) data are included for reference. (e) Representative M-modes of Tcp-1eta mutant flies exhibiting lack of TRF-driven cardioprotection. (f) Heart period and (g) arrhythmia index, and (h) representative M-modes show improved cardiac function in 5-week old ALF flies with heart specific knockdown of mitochondrial ETC genes relative to 5 week old male WT flies (n≥24). 3 and 7-week old male WT data are included for reference. *;p<0.05, Mann Whitney test. Error bars: s.e.m.