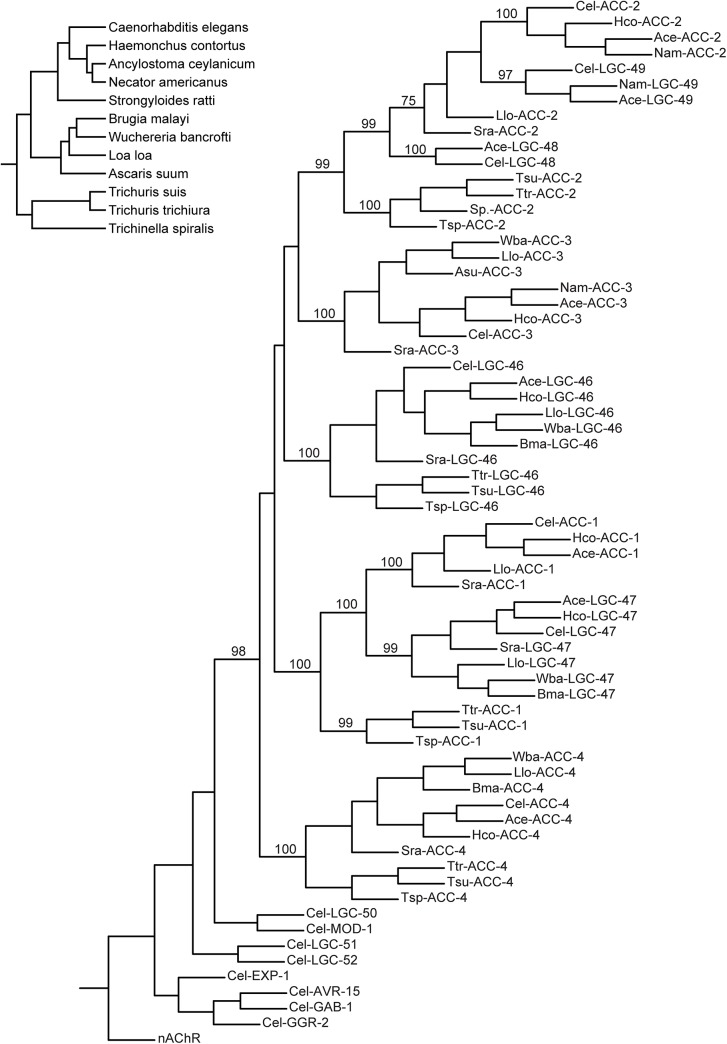
Fig 1. Phylogenetic tree of ACCs in C. elegans and parasitic nematode species.
A maximum likelihood tree made from predicted protein sequences identified using C. elegans (cel) ACCs as BLAST queries for similar sequences in Haemonchus contortus (Hco), Ancylostoma ceylanicum (Ace), Necator americanus (Nam), Strongyloides ratti (Sra), Brugia malayi (Bma), Wuchereria bancrofti (Wba), Loa loa (Llo), Ascaris suum (Asu), Trichuris suis (Tsu), Trichuris trichiura (Ttr), and Trichinella spiralis (Tsp). Bootstrap values out of 100 are indicated at ACC clade-defining branches. The tree was rooted to the α1 subunit of the torpedo nicotinic AChR [81]. Representative subunits from other C. elegans chloride-selective pLGIC clades (LGC-50, LGC-51, LGC-52, MOD-1, EXP-1, AVR-15, GAB-1, and GGR-2) were also included to ensure that predicted ACC orthologs from other species grouped with the celACCs instead of other C. elegans chloride channels. Inset: Phylogenetic relationship of nematodes species. Branch lengths are approximate.