Figure 4.
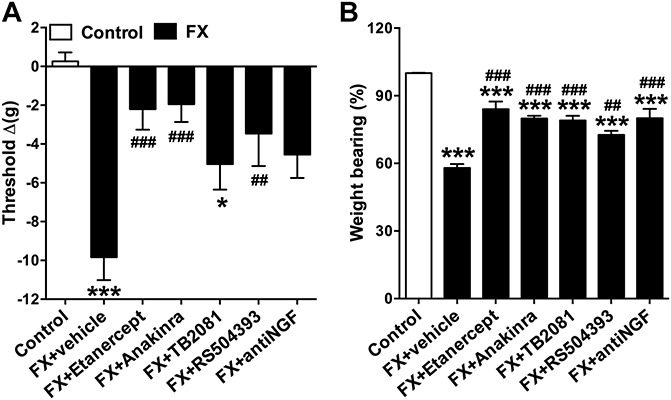
Spinally administered inflammatory mediator receptor antagonists/inhibitors reduced allodynia and unweighting at 4 weeks after fracture. Fracture (FX) rats were intrathecally injected with either: (1) vehicle, (2) the TNF inhibitor etanercept (100 μg), (3) the IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra (100 μg), (4) the IL-6 receptor antagonist TB-2081 (20 μg), (5) the chemokine (C-C motif) receptor type 2 (CCR2) antagonist RS504393 (3 μg), and (6) the anti-nerve growth factor (NGF) antibody muMab 911 (12.4 μg). Behavioral testing was performed at various time intervals after intrathecal injection based on preliminary pilot time course studies identifying the peak analgesic effects for each drug (etanercept 3 hours, anakinra 30 minutes, TB2081 15 minutes, and RS504393 and muMab 911 1 hour). All receptor antagonists/inhibitors reduced postfracture hind paw allodynia (A) and unweighting (B). There were no effects on hind paw temperature or thickness. Values are mean ± SE, n = 8 per cohort. One-way analysis of variance (P < 0.001) with Bonferroni post hoc testing *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 for FX + vehicle, FX + etanercept, FX + anakinra, FX + TB2081, FX + anti-NGF antibody or FX + RS504394 vs control, ##P < 0.01 and ###P < 0.001 for FX + etanercept, FX + anakinra, FX + TB2081, FX + anti-NGF antibody, or FX + RS504394 vs FX + vehicle.
