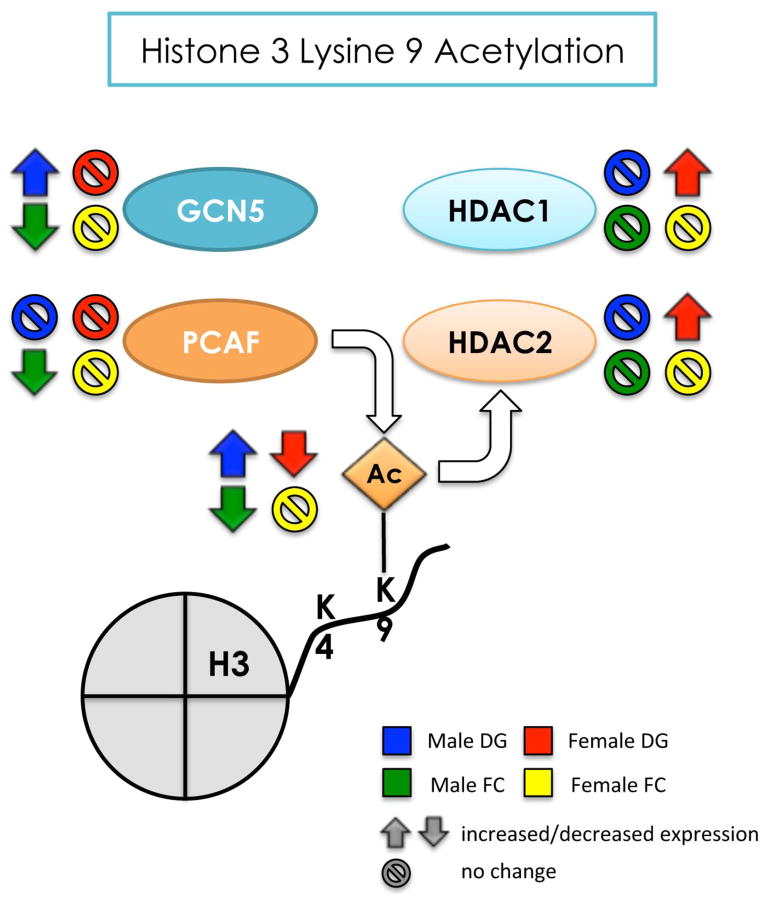
Figure 10. Summary of the effects of developmental arsenic exposure on acetylation of H3K9 and its associated chromatin modifying proteins in the adult brain.
This figure displays the significant effects of DAE on levels of H3K9ac (next to the Ac group) and protein expression of GCN5 and PCAF (histone acetyltranferases) and HDAC1 and HDAC2 (histone deacetylases) in the adult brain. DAE has a differential impact on H3K9ac levels and histone acetyltransferase protein expression in the male brain: DAE increases levels of H3K9ac in the male dentate gyrus likely due to increases in GCN5 (blue) and decreased H3K9ac in the frontal cortex, likely due to both decreased GCN5 and PCAF (green). As observed with H3K4me3, DAE results in the opposite patterns of expression in the female dentate gyrus for H3K9ac and associated chromatin modifying proteins compared to the male dentate gyrus. DAE decreases H3K9ac in the female DG like due to increased protein expression of HDAC1 and HDAC2 (red arrows) with no impact on GCN5 or PCAF. Interestingly, DAE preferentially alters histone deacetylase protein expression in females and histone acetyltransferase protein expression in males, with levels of H3K9ac affected by DAE dependent on both region and sex.
Up arrow = significantly increased expression
Down arrow = significantly decreased expression
Circle w/ line = no significant change in levels or expression
blue = male dentate gyrus; green = male frontal cortex
red = female dentate gyrus; yellow = female frontal cortex