Figure 5. Developmental arsenic exposure increases acetylation of histone 3 lysine 9 (H3K9ac) and protein expression of the histone acetyltransferase, GCN5, in the adult male dentate gyrus.
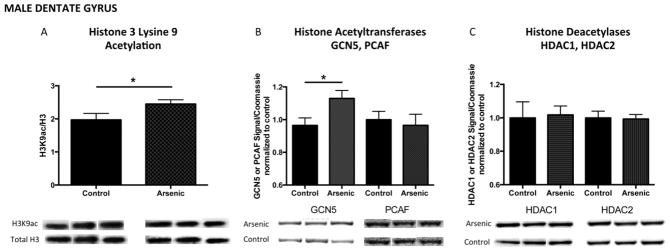
H3K4me3 is associated with histone acetylation for transcriptionally active genes. As observed with H3K4me3, developmental arsenic exposure significantly increases levels of H3K9ac in (A) the male dentate gyrus. DAE increases protein expression of histone acetyltransferase (B, left) GCN5 but not histone acetyltransferase (C, right) PCAF, both capable of acetylation of H3K9. Protein expression of histone deacetylases (C) HDAC1 and HDAC2 is not impacted by DAE in the male dentate gyrus. *p<.05; **p<.01
