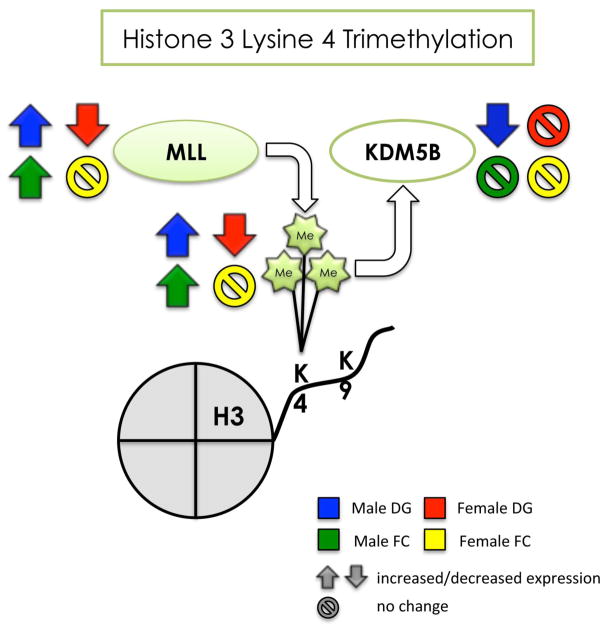
Figure 9. Summary of the effects of developmental arsenic exposure on trimethylation of H3K4 and its associated chromatin modifying proteins in the adult brain.
This figure displays the significant effects of DAE on levels of H3K4me3 (next to the Me groups) and protein expression of MLL (histone methyltransferase) and KDM5B (histone demethylase) in the adult brain. DAE impacts H3K4me3 levels and MLL protein expression in a similar manner in both tissue types of the male brain (blue and green arrows), suggesting increased transcriptional activation in the male brain. The effect of DAE in KDM5B is only apparent in the male dentate gyrus (blue), and inversely correlates with protein expression levels of MLL. DAE results in the opposite effect in the female brain, with decreased H3K4me3 and MLL protein expression (red arrows), but only in the dentate gyrus; the female frontal cortex is relatively unaffected by DAE (yellow). DAE impacts H3K4me3 primarily in a sex- specific manner with regional differences apparent in the female brain.
Up arrow = significantly increased expression
Down arrow = significantly decreased expression
Circle w/ line = no significant change in levels or expression
blue = male dentate gyrus; green = male frontal cortex red = female dentate gyrus; yellow = female frontal cortex