Figure 6.
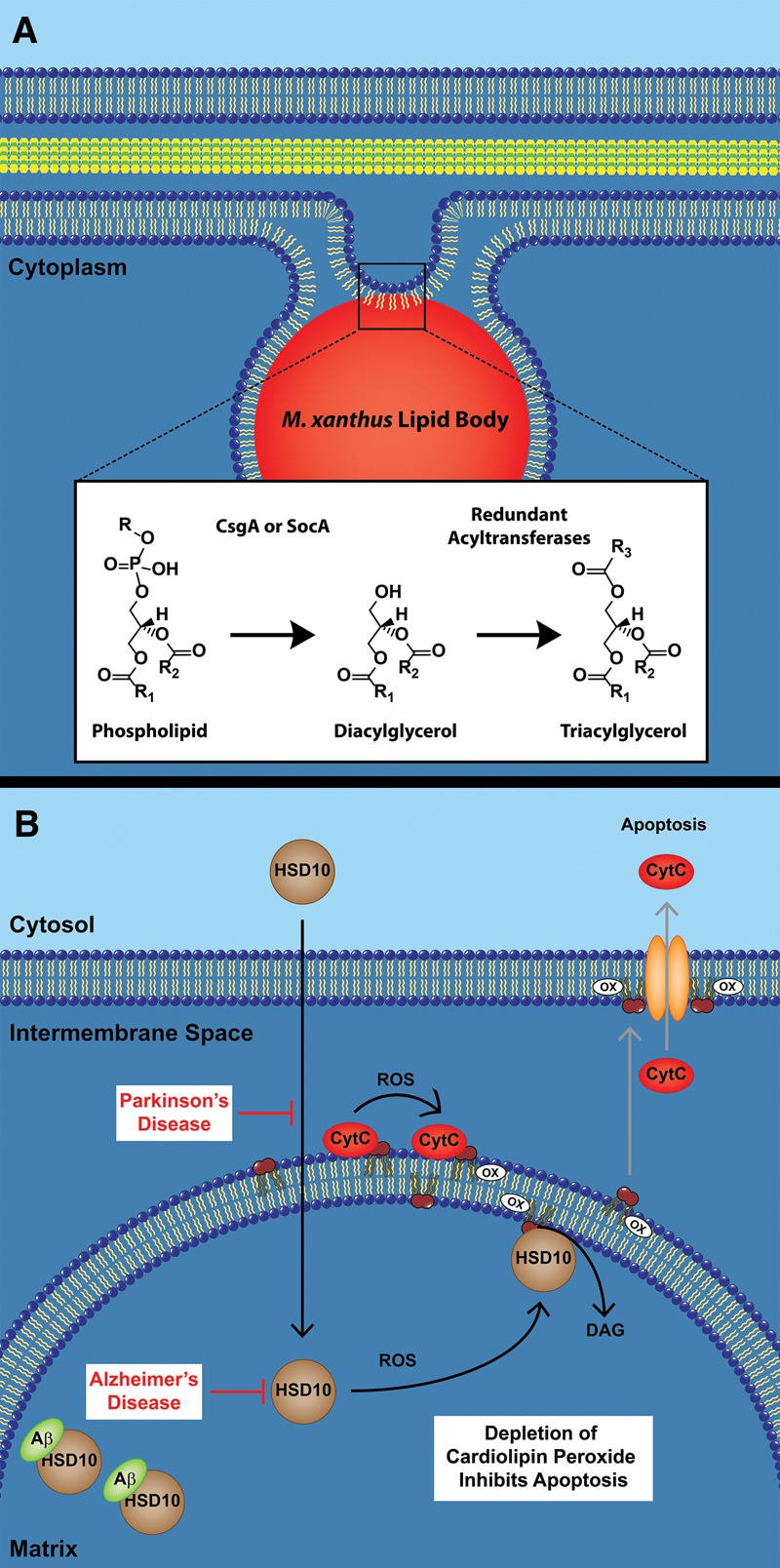
Proposed functions of CsgA and HSD10 in Myxococcus and humans. (A) M. xanthus lipid bodies are synthesized from existing membrane phospholipids. This reaction is proposed to occur directly from the breakdown of PG and CL into DAGs by CsgA. An as yet uncharacterized acyltransferase could then convert the DAGs into TAGs. (B) In the presence of ROS created from oxidative stress, HSD10 is recruited to the inner mitochondrial membrane where CytC simultaneously converts CL to CLox. HSD10 removes CLox before it is exported to the outer membrane, and CytC is released, inhibiting apoptosis. In Parkinson's disease, HSD10 levels within the mitochondria are greatly diminished. In Alzheimer's disease, HSD10 is inactivated within the matrix by the binding of the Aβ peptide. In both instances, oxidative damage occurs, leading to apoptosis.
