Figure 3.
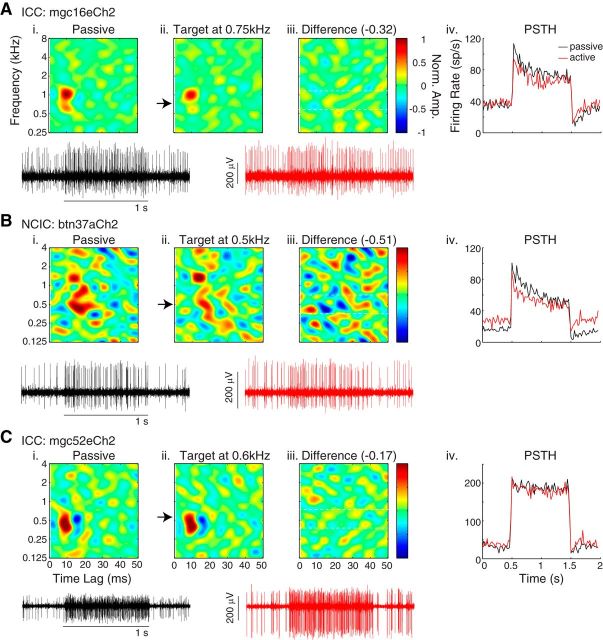
Examples of task-related plasticity in the IC. A, STRF of an ICC neuron estimated by reverse correlation with the reference noise sounds in the passive (i) and active (ii) behavioral condition. The STRF heatmap indicates the stimulus frequencies and time lags correlated with excited (red) or suppressed (blue) neural spike rate. STRFs have been interpolated for display purposes only. The arrow indicates target frequency. The difference between active and passive STRFs (iii) shows slight suppression near the target frequency. Local STRF changes were measured in a one-octave band (white dotted lines) centered at the target frequency. The PSTH (iv), computed by averaging across all reference TORC responses, is suppressed in the active (red) condition. The raw waveform of the spike responses to one reference stimulus in the passive (black) and active (red) conditions is shown at the bottom. The black bar indicates the duration of the 1 s stimulus. B, Same format as A for an NCIC neuron with a suppressed receptive field during behavior. C, Same format as A for an ICC neuron with no receptive field change in the active condition. In this recording, the raw spike waveform (bottom) was larger during behavior but the unit isolation remained stable. norm. amp., normalized amplitude; sp/s, spikes/second.