Figure 7.
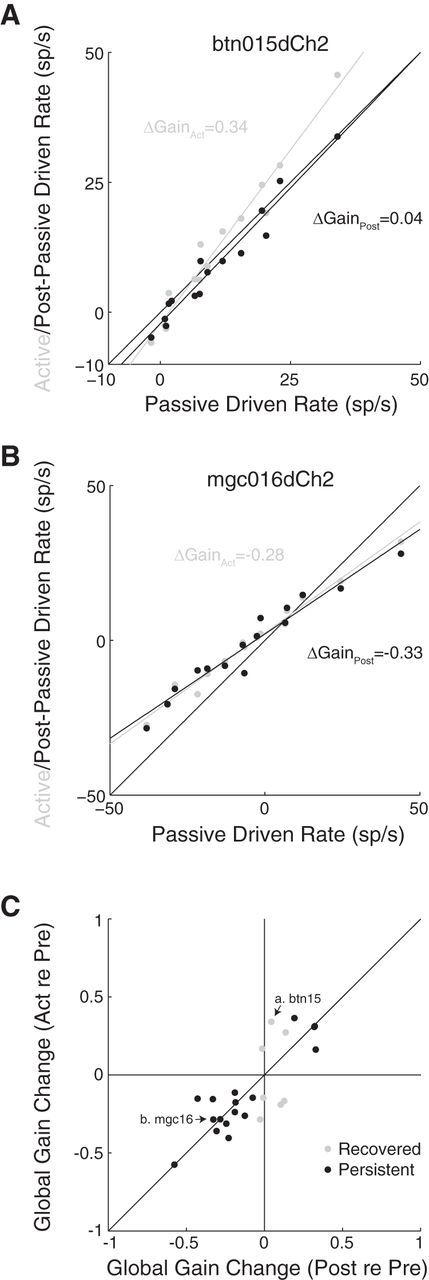
Recovery and persistence of task-related plasticity. A, Active (gray) and postpassive (black) driven firing rate versus prepassive driven firing rates for an ICC neuron. The global gain change is positive (slope, >1) and recovers in the postpassive condition immediately following the behavior (global gain change, 0; postpassive relative to prepassive). B, Same format as A for a different ICC neuron with a negative global gain change that persists in the postpassive condition. C, Global gain changes relative to prepassive in the active (Act re Pre) versus postpassive (Post re Pre) condition in 24 of 40 neurons with significant changes during behavior. The global gain change recovered completely in 7 neurons (gray) and persisted or only partially recovered in the remaining 17 neurons (black). Arrows indicate the examples in A and B. sp/s, spikes/second.
