Figure 8.
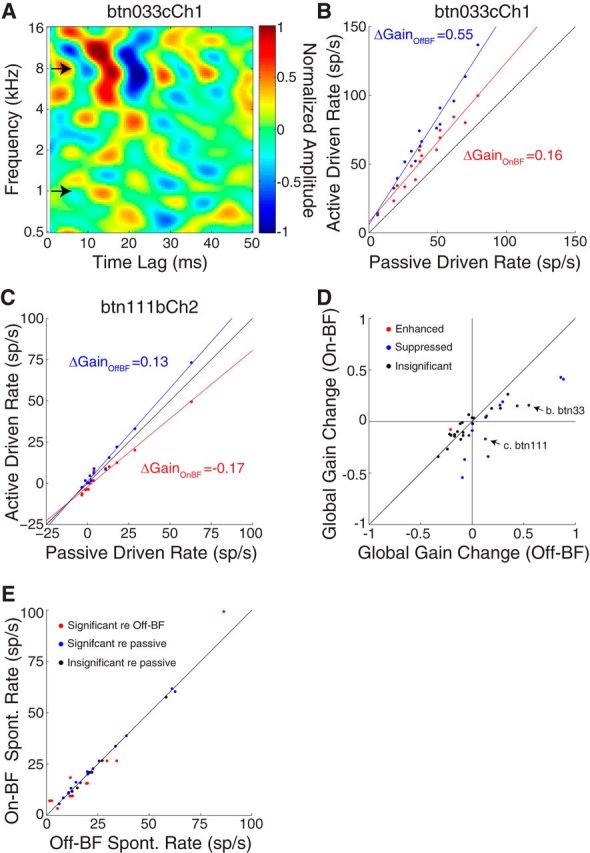
Task-related plasticity depends on target frequency. A, STRF from an ICC neuron showing the frequencies (arrows) of On-BF (8 kHz) and Off-BF (1 kHz) targets for two consecutive behavior sessions. B, Driven firing rates measured in active condition for the On-BF target (red) and Off-BF target (blue) versus prepassive driven rates for the neuron in A. The global gain change is positive for the On-BF target and further enhanced for the Off-BF target. C, On-BF versus Off-BF gain comparison for a different ICC neuron, plotted as in B. Relative to passive, the global gain change is negative for the On-BF target and positive for the Off-BF target. D, Scatter plot of the global gain changes for On-BF targets versus Off-BF targets (1–3 octaves above or below BF). In 20 of 34 cases, responses did not change significantly during behavior and/or between targets (black). In 13 of 14 of the remainder, global gain was suppressed (blue) for On-BF relative to Off-BF and the median difference was significant (−0.23, p = 0.002, signed-rank test). Arrows indicate the example neurons in B and C. E, Spontaneous (spont.) rate during behavior sessions with On-BF versus Off-BF targets. Colors indicate spontaneous rates that did not change during behavior (behaving vs passive, black), that changed during behavior but did not depend on the target frequency (blue), or that changed significantly between On-BF and Off-BF target behaviors (red). sp/s, spikes/second.
