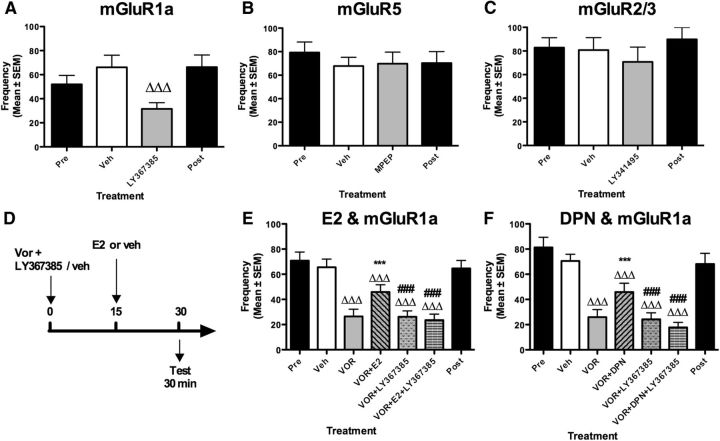
Figure 5.
Effects of acute blockade of mGluRs on the frequency of RCSMs. A–C, The specific antagonist of mGluR1a (LY367385) inhibits RCSM frequency (100 μg, n = 12, A) within 30 min, while specific antagonists of mGluR2/3 (LY341495) and mGluR5 (MPEP) have no effect on RCSM within 30 min (100 μg, n = 9 and 8 respectively, B, C). D, The combined effect of mGluR1a blockade and E2 was tested following acute blockade of brain aromatase using the described experimental design. E, F, Blockade of local estrogen synthesis by the aromatase inhibitor VOR (50 μg) inhibits RCSM frequency within 30 min. E2 or DPN (50 μg; E, F) injected 15 min after VOR prevents the effect of VOR on RCSMs. LY367385 (100 μg) prevents the restoration of behavior by E2 (E, n = 22) or DPN (F, n = 15). The Pre and Post black bars provide reference behavior frequencies after vehicle intracerebroventricular injections performed before and after the acute treatments, but these data are not included in the statistical analyses. ΔΔΔp < 0.001 versus vehicle (Veh) by Fisher's LSD post hoc test (A) and Newman–Keuls post hoc test; ***p < 0.001 versus VOR; ###p < 0.001 versus VOR + E2 or VOR + DPN by Newman–Keuls post hoc tests after identification of a significant treatment effect (repeated measure) by two-way ANOVA.