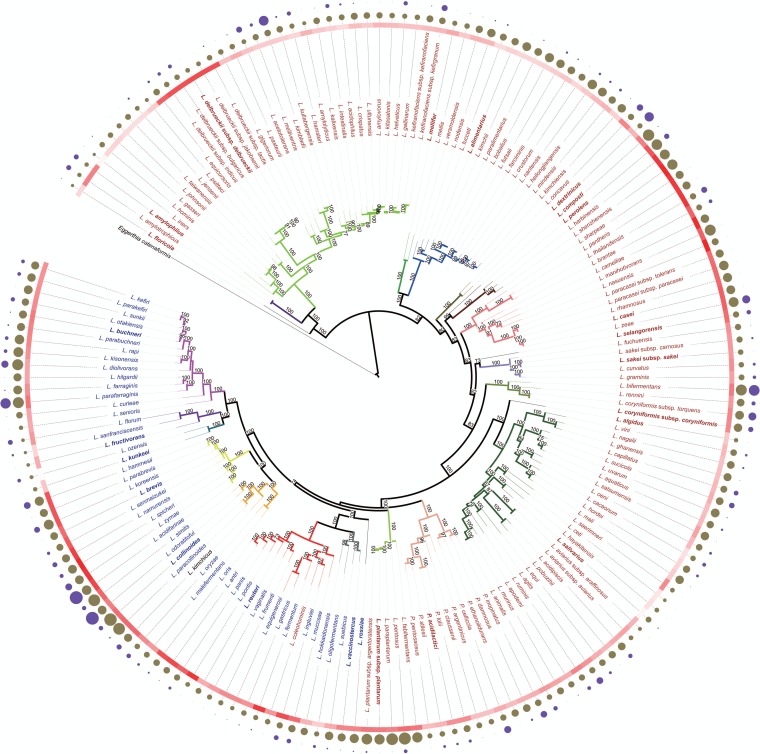
FIG 1.
Phylogenomic analysis and basic features of 174 Lactobacillus and Pediococcus type strains based on the concatenated protein sequences of single-copy core genes. Eggerthia catenaformis was used as an outlier for the phylogenetic analysis. The maximum likelihood tree was inferred by PhyML using the best model (LG+I+G+F) predicted by ProtTest. Bootstrap support values were calculated from 1,000 replicates, and only values above 70% are shown in the figure. Members of the same group are indicated by the same color for branches, and the type strain of each group is printed in bold. Names of homofermentative species are printed in red; names of heterofermentative species are printed in blue. The color gradient in red represents the GC content of each genome sequence; higher GC contents are indicated by darker shading. The solid circles in brown represent genome sizes of these type strains; the area of the circle correlates with the genome size. The solid circles in dark purple represent the number of CRISPR spacers (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) in each genome; the area of the circles correlates with the number of spacers. The assignment of species to phylogenetic groups shown here confirms previous assignments of species to phylogenetic groups (14) with the following exceptions or additions: L. kunkeei and Lactobacillus ozensis are now grouped together in a new L. kunkeei group; Lactobacillus selangorensis (previously in the L. perolens group) forms a separate group adjacent to L. sakei; L. amylophilus (previously in the L. delbrueckii group) forms a separate group adjacent to the L. delbrueckii group; Lactobacillus algidus (previously L. salivarius) forms a separate group adjacent to the L. salivarius group. Lactobacillus concavus was assigned to a new group with the reclassified L. dextrinicus (93). L. mellis and L. mellifer (66) form a separate group.