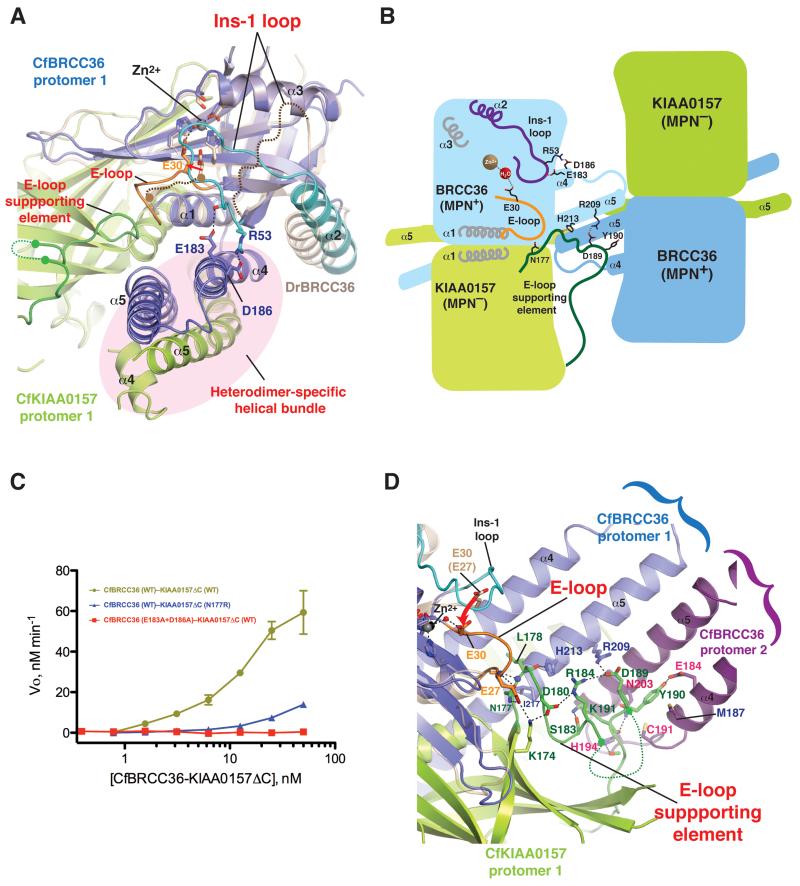
Figure 5. The active site conformation of BRCC36 is dependent on heterodimerization with KIAA0157.
A) Zoom in comparison of the heterodimer interface of the CfBRCC36–KIAA0157ΔC complex (blue–green) superimposed on the homo dimerization interface of DrBRCC36 (wheat). The Ins-1 loop (cyan) of CfBRCC36 contacts helix α4 (blue) within the coiled coil helical bundle region (CCHB; highlighted by pink oval). Both regions in the DrBRCC36 homodimer are disordered. The E-loop of CfBRCC36 and E-loop supporting element of CfKIAA0157 are colored orange and green respectively. Disordered regions are shown as curved dashed lines.
B) Schematic of inter-subunit interactions shown in panels A & D that support a productive conformation of the BRCC36 active site. The integrity of the helical bundle involving helices α4 and α5 of BRCC36 and KIAA0157 is dependent on BRCC36–KIAA0157 heterodimerization. Within one protomer of BRCC36, the Ins-1 loop is buttressed by contacts with helix α5. Across the BRCC36–KIAA0157 heterodimer, the E-loop of BRCC36 is buttressed by contacts with the “E-loop supporting element” of KIAA0157. The “E-loop supporting element” of KIAA0157 in turn is buttressed by contacts with helices α4 and α5 within the BRCC36–KIAA0157 heterodimer and also across the super dimer of BRCC36–KIAA0157 heterodimers. For clarity, detailed features are only drawn on one heterodimer. Not to scale.
C) Cleavage activity of the WT CfBRCC36–KIAA0157ΔC complex and the indicated mutants towards an internally quenched K63-diUb fluorogenic substrate. Results ± SEM are the average of three independent experiments carried out in duplicate. Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE and SEC-MALS analysis of the indicated complexes are shown in Figure S7D, E.
D) Zoom in view of the heterodimer and super dimer interface of the CfBRCC36–KIAA0157ΔC complex (blue-green). The E-loop (orange) of CfBRCC36 contacts the E-loop supporting element (green) of CfKIAA0157. The E-loop supporting element of CfKIAA0157 in turn contacts the CCHB (specifically helix α5) of CfBRCC36 (denoted as protomer 1). In addition, the E-loop supporting element of CfKIAA0157 also makes contact to the CCHB of CfBRCC36 (purple-denoted protomer 2), of a second CfBRCC36-KIAA0157 heterodimer arranged in the super dimer configuration shown in Figs. 1B & 6A. Disordered regions in the DrBRCC36 MPN+ domain are shown as curved dashed lines. See also Figures S3, S7 and S8.