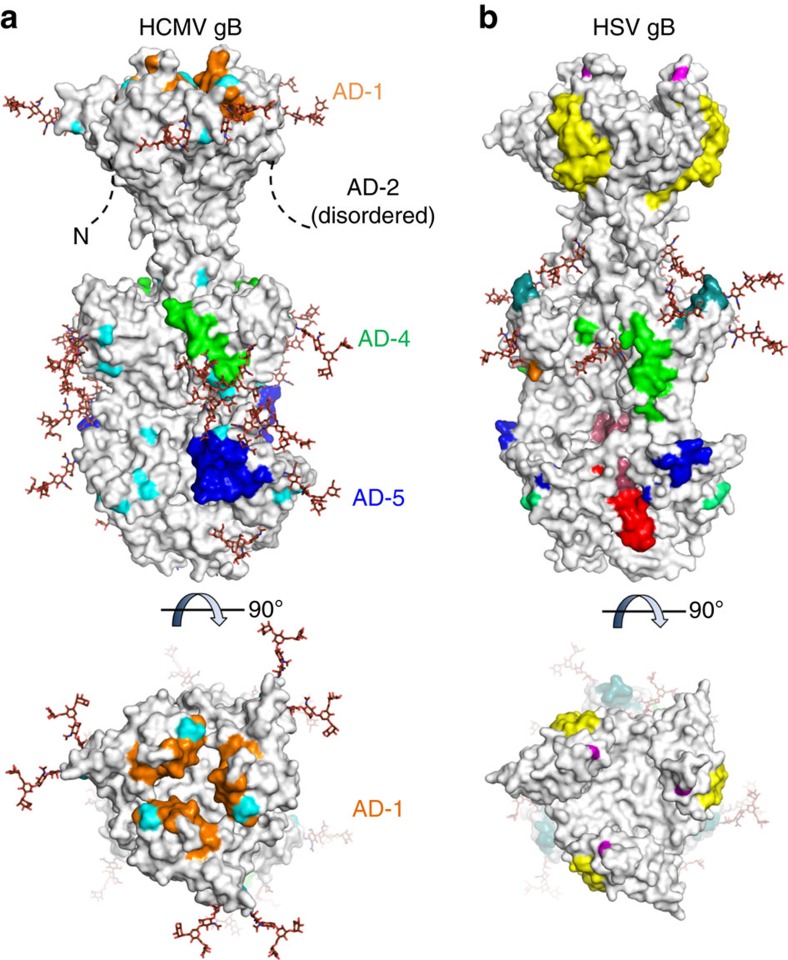
Figure 6. Neutralizing epitopes in HCMV gB.
(a) Surface representation of HCMV gB in its postfusion conformation with known neutralizing epitopes in AD-1 (domain IV) in orange, AD-4 (domain II) in green and AD-5 (domain I) in blue. These epitopes are composed of residues Tyr280-Phe300 in AD-5 (mAb 1G2, this report), residues Ala360-Tyr364 and Ser377-Asp385 in AD-4 (mAb SM5 (ref. 37)) and residues Pro571-Val580 and His606-Phe619 in AD-1 (mAbs ITC48, ITC52, ITC63B and ITC63C32). The epitopes in AD-4 and AD-5 have been defined based on crystal structures while the epitope in AD-1 was identified through peptide mapping. Polymorphisms among clinical and laboratory strains of HCMV are shown in cyan. (b) Surface representation of HSV gB (PDB ID: 2GUM) with neutralizing epitopes defined through peptide mapping and single amino acid resistant mutant studies11,31,64. Residues recognized by mAbs H233 (Ala315 and Arg328), H126 (Tyr303), H1375 (Arg304), B4 (Glu305) and H1435 (His308) are shown in blue; mAb SS55 (Asp199 and Ala203) in light green; mAb H1781 (Pro454-Ser473) in teal; mAb H1838 (Ala390-Gly410) in green; mAb C226 (Asp419) in orange; mAb SS10 (Tyr640-Phe670) in yellow; mAbs B2 and B5 (Gly594) in magenta; mAb SS106 (Ser697-Ala725) in pink; mAb SS144 (Arg715-Ala725) in red. Simple (oligomannose) glycans shown as brown sticks were modelled into glycosylation sites in the primary sequence of HCMV and HSV gB using the Glyprot server.