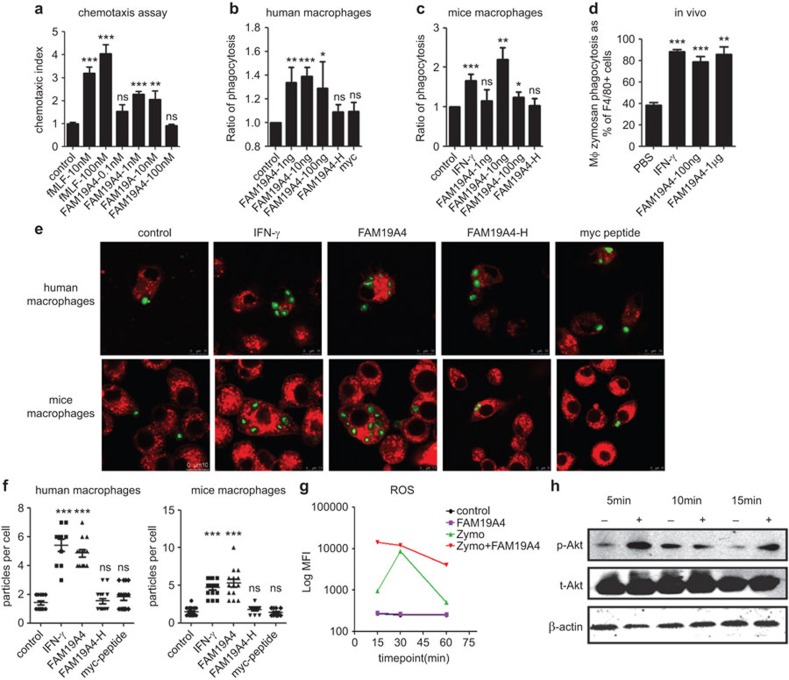
Figure 3.
FAM19A4 chemo-attracts macrophages and promotes the phagocytosis of macrophages both in vitro and in vivo. (a) The chemotactic activity of FAM19A4 on human macrophages. FAM19A4 promotes the phagocytosis of human macrophages derived from monocytes (b, e) and RAW264.7 cells (c, e); this was analyzed using flow cytometry or confocal microscopy. (d) FAM19A4 increases the phagocytosis of mouse peritoneal resident macrophages in vivo; this was also analyzed by flow cytometry. There were at least five mice in each group. (f) The calculation of the number of FITC-zymosan particles that were swallowed by a single macrophage; this was imaged by confocal microscopy (n>10). (g) FAM19A4 promotes ROS release upon zymosan stimulation in mice peritoneal macrophages. The relative fluorescence intensity is taken as the average of the values from four repeated experiments. (h) The RAW264.7 cells were pre-treated for 2 h in the presence or absence of FAM19A4 and were then challenged with zymosan (100 µg/ml) at different time points. The expression of total protein and the phosphorylated forms of Akt were determined by western blotting. The result of one experiment, representative of four total experiments, is presented.