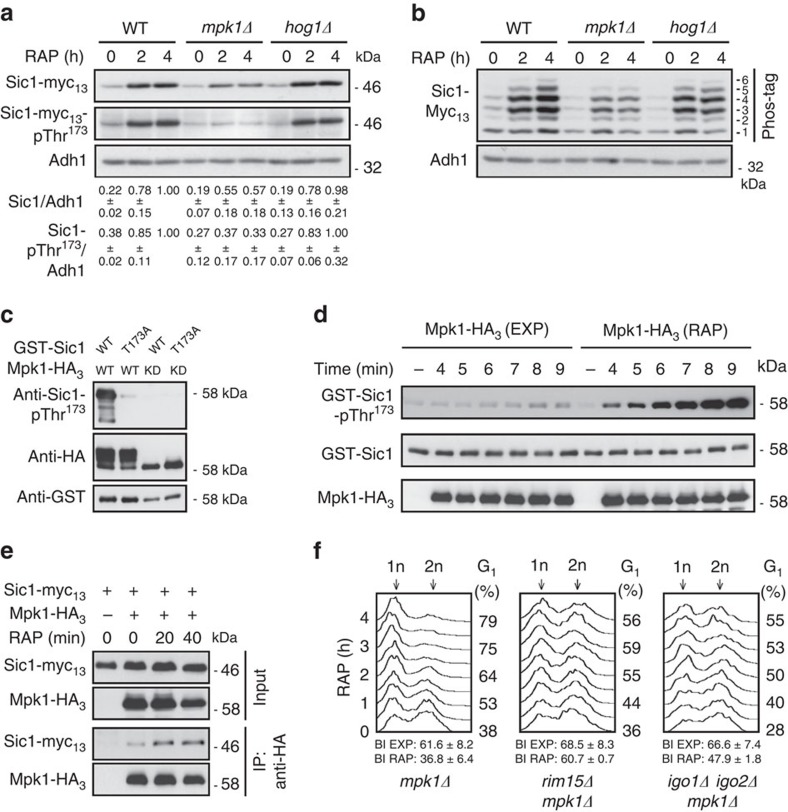
Figure 4. Mpk1 phosphorylates Thr173 in Sic1.
(a) Mpk1, but not Hog1, is required for normal Sic1 accumulation in rapamycin-treated cells. Levels of Sic1-myc13 and of Sic1-myc13-pThr173 signals were determined in cells with the indicated genotypes before (0 h) and following a rapamycin treatment (for 2 and 4 h). The Sic1-myc13 levels or Sic1-myc13-pThr173 signals (three independent experiments) were normalized to Adh1 in each case, calculated relative to the value in 4-h rapamycin-treated wild-type cells (set to 1.0), and expressed as mean values (±s.d.). (b) Phos-tag phosphate affinity gel electrophoresis analysis of genomically myc13-tagged Sic1 from exponentially growing (time 0 h) and rapamycin-treated (2 and 4 h) WT, mpk1Δ and hog1Δ cells were carried out as in Fig. 2c. (c) Mpk1 phosphorylates Thr173 in Sic1 in vitro. Mpk1-HA3 and kinase-dead Mpk1KD-HA3 (carrying the K54R mutation) were purified from rapamycin-treated (1 h) cells and used for in vitro protein kinase assays on bacterially purified GST-Sic1 or GST-Sic1T173A. Levels of Sic1 protein and of Sic1-pThr173 signals were determined using anti-GST and anti-Sic1-pThr173 antibodies, respectively. Immunoblot analysis using anti-HA antibodies served as input control for Mpk1-HA3 variants. Mpk1-HA3, but not Mpk1KD-HA3, displayed slow-migrating isoforms due to post-translational modifications. (d) Rapamycin treatment strongly stimulates Mpk1 protein kinase activity towards Thr173 in Sic1. In vitro protein kinase assays were carried out as in c for the indicated times using Mpk1-HA3 preparations from exponentially growing (EXP) or rapamycin-treated (1 h; RAP) cells. (e) Rapamycin treatment stimulates the interaction between Sic1-myc13 and Mpk1-HA3. Plasmid-encoded Mpk1-HA3 was immunoprecipitated from extracts of untreated (0 min) and rapamycin-treated (RAP; 20 and 40 min) Sic1-myc13-expressing WT cells. Cells carrying an empty vector (−) were used as control. The co-precipitated Sic1-myc13 levels were detected by immunoblot analysis using anti-myc antibodies. (f) Proper G1 arrest in rapamycin-treated cells requires Mpk1. FACS analyses (see Supplementary Fig. 6 for quantifications of triplicates) and BI determinations were performed as in Fig. 1a. All strains (relevant genotypes indicated) are isogenic to JK9-3D (see Fig. 1b,c for comparison). FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting.