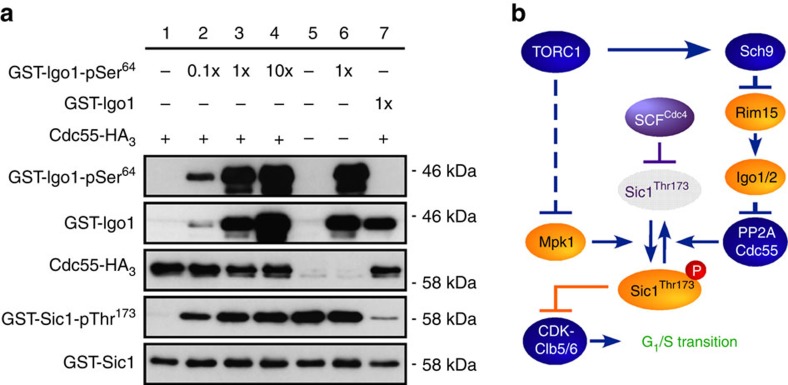
Figure 5. TORC1 coordinates G1–S cell cycle progression via Mpk1 and PP2ACdc55.
(a) PP2ACdc55 dephosphorylates pThr173 in Sic1 and this activity is inhibited in a concentration-dependent manner by activated Igo1 (Igo1-pSer64), but not inactive Igo1. GST-Sic1 was phosphorylated by Mpk1 in vitro before being used as a substrate for the PP2ACdc55 phosphatase assay. Phosphatase activity of PP2ACdc55 was analysed in the absence (lane 1) and in the presence of increasing amounts (lanes 2, 3 and 4, respectively) of recombinant Igo1-pSer64, which had been subjected to thio-phosphorylation by Rim15 previously. Assays without both PP2ACdc55 and Igo1-pSer64 (lane 5), without PP2ACdc55 but with Igo1-pSer64 (lane 6), and with PP2ACdc55 combined with inactive Igo1 (lane 7) were included as additional controls. The levels of Ser64 phosphorylation in GST-Igo1 (GST-Igo1-pSer64), GST-Igo1, Cdc55-HA3, Thr173 phosphorylation in GST-Sic1 (GST-Sic1-pThr173) and GST-Sic1 were determined by immunoblot analyses using phospho-specific anti-Igo1-pSer64, anti-GST, anti-HA, phospho-specific anti-Sic1-pThr173 and anti-GST antibodies, respectively. (b) Model for the role of TORC1 in regulating the phosphorylation status and stability of the CDKI Sic1. For the sake of clarity, we have not schematically depicted the additional role of Rim15-Igo1/2 in G1 cyclin downregulation that may transiently favour CDK-mediated multi-site phosphorylation and consequently SCFCdc4-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of Sic1 following TORC1 inactivation. Sic1 inhibits the CDK–Clb5/6 complexes to prevent transition into S phase43. Arrows and bars denote positive and negative interactions, respectively. Solid arrows and bars refer to direct interactions, the dashed bar refers to an indirect interaction. For details see text.