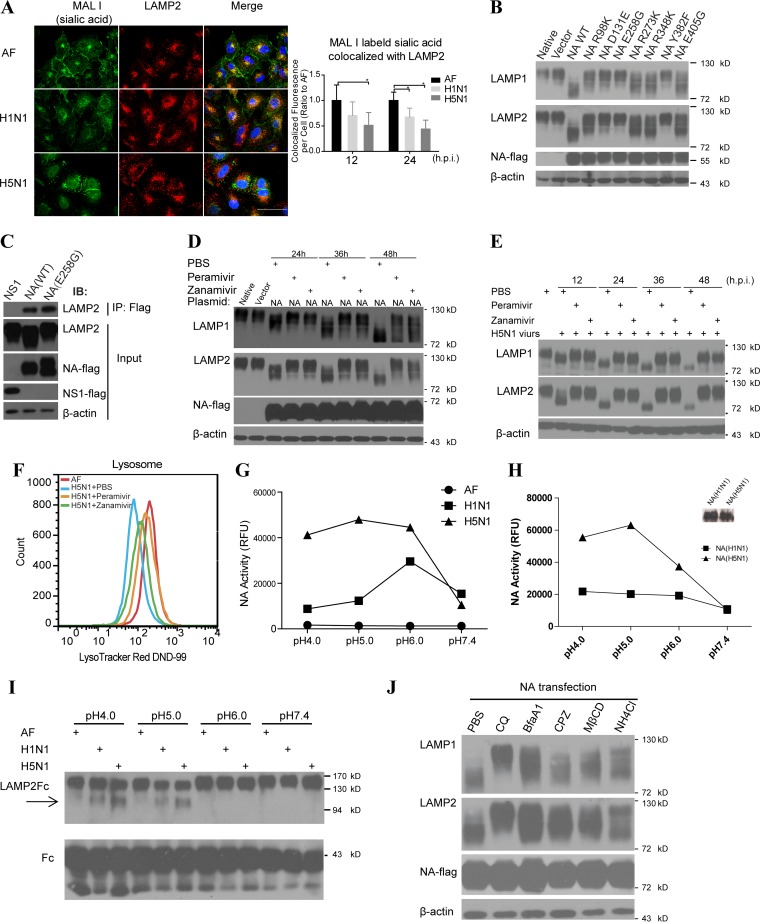
FIG 5.
Influenza virus NA induced the LAMP deglycosylation depending on the its NA activity and low-pH environment. (A) Immunofluorescent colocalization of MAL I-labeled sialic acid and lysosomal membrane marker LAMP2 in A549 cells infected with H1N1 or H5N1 virus or treated with vehicle as a control. The sialic acid fluorescence signal colocalized with LAMP2 per cell (on the right) was estimated by examining 50 to 100 cells. Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) Immunoblot analysis of LAMP1 and LAMP2 deglycosylation in 293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding vector, wild-type (WT) NA, or mutant NAs using NA-flag as an overexpression control and β-actin as a loading control. (C) 293T cells were transfected with NS1-flag, wild-type NA-flag, or mutant NA (E258G) encoding plasmids, respectively, and the immunoprecipitation (IP) assay was performed with anti-flag antibody. Cell lysates (input) and immunoprecipitated complexes were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-LAMP2 and anti-flag antibodies. (D) 293T cells were transfected with control plasmid or NA(H5N1)-encoding plasmids. After 6 h, peramivir (30 μg/ml), zanamivir (30 μg/ml), or PBS was separately added into the media of these cultured cells. The deglycosylation of LAMP1 and LAMP2 was analyzed by immunoblotting, and flag was used for NA detection and β-actin as a loading control. (E) Immunoblot analysis of LAMP1 and LAMP2 deglycosylation in A549 cells infected with H5N1 virus and treated with PBS, peramivir (30 μg/ml), or zanamivir (30 μg/ml), respectively, at the indicated time points. (F) FACS analysis of the lysosome numbers in A549 cells treated with AF and in cells infected with H5N1 virus and treated with peramivir (30 μg/ml), zanamivir (30 μg/ml), or PBS. (G) Assay of NA activity of H1N1 or H5N1 influenza virus or vehicle control AF in different buffers (pH 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, or 7.4) at 37°C. RFU, relative fluorescence units. (H) Activity assay evaluating 0.1 μg of H1N1 or H5N1 influenza virus NA protein in different buffers (pH 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, or 7.4) at 37°C. The amounts of NA protein were also determined by immunoblot analysis (shown on the right). (I) The extracellular region of LAMP2 fused to the human IgG-Fc fragment (LAMP2-Fc) and the control protein human IgG-Fc (Fc) were conjugated to protein A-beads. After incubation with vehicle or H1N1 or H5N1 virus in different buffers (pH 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, or 7.4) at 37°C for 6 h, protein changes were detected by immunoblotting with anti-LAMP2 antibody or Fc antibody as a control. (J) 293T cells were transfected with NA(H5N1) gene and treated with control PBS, chloroquine (CQ), bafilomycin A1 (BfaA1), chlorpromazine (CPZ), methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD), or NH4Cl, and then, 48 h later, LAMP1 and LAMP2 were detected by immunoblotting with NA-flag as an overexpression control and β-actin as a loading control. All data represent means ± the SEM of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.