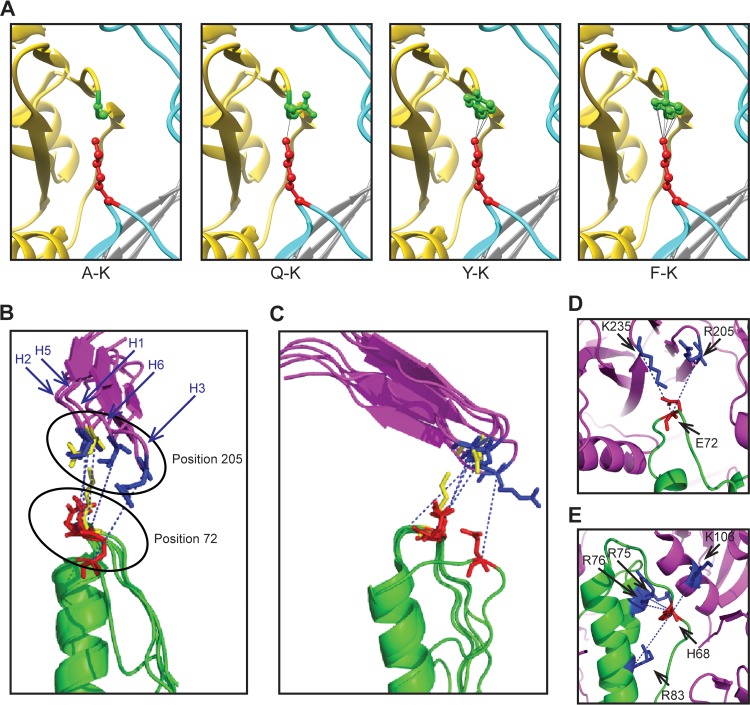
FIG 7.
Intermonomer interactions between HA1 and HA2. (A) The intermonomer interactions between HA1 residue 205 and HA2 residue 72 are modeled for the A-K, Q-K, Y-K, and F-K pairs using the structure with PDB accession number 3M6S. The HA1 residues (A, Q, Y, and F) at position 205 are shown in green. The K residue at residue 72 of HA2 is shown in red. (B and C) Different rotational perspectives of the local environment surrounding the intermonomer interface between HA1 residue 205 and HA2 residue 72 of different HA subtypes (H1, PDB accession number 1RU7; H2, PDB accession number 3QQB; H3, PDB accession number 2HMG; H5, PDB accession number 2IBX; H6, PDB accession number 4XKF). For clarity, only residues 198 to 213 in HA1 are shown and illustrated as purple ribbons. Positions 72 and 205 from the H1 subtype are shown in yellow. For other subtypes, residue 72 of HA2 is shown in red, while residue 205 of HA1 is shown in blue. The blue dotted lines indicate the direction between C alpha carbons for the respective residue pairs. (D and E) Alternate interfaces between HA1 and HA2 are shown for subtype H3 (PDB accession number 2HMG) (D), and alternate interfaces between two adjacent HA2 monomers and HA1 are shown for subtype H6 (PDB accession number 4XKF) (E). Residue positions are indicated. Magenta, HA1; green, HA2.