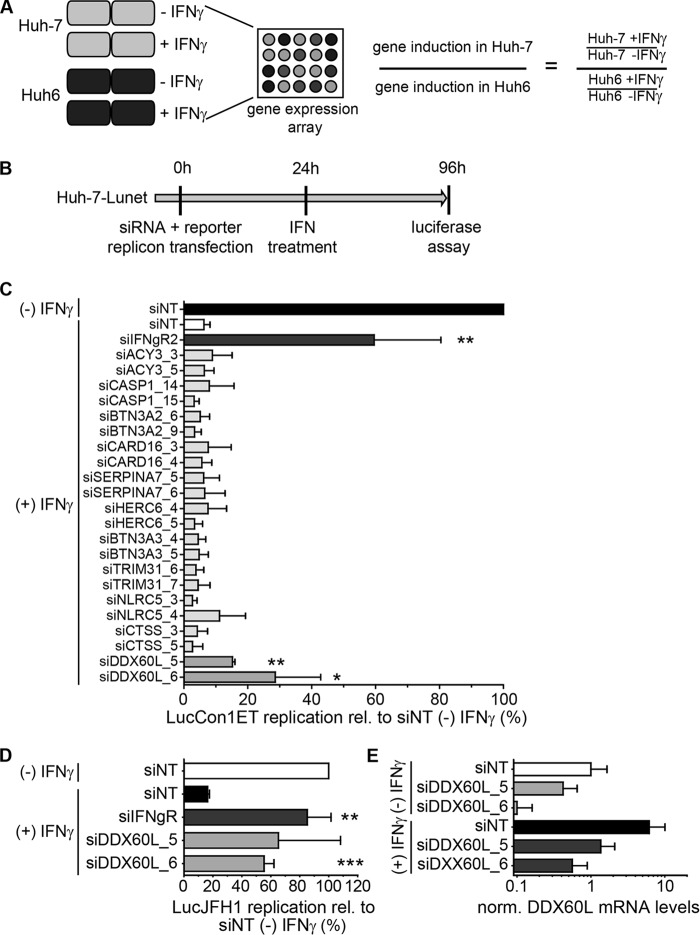
FIG 2.
Identification of effector proteins of the IFN-γ response against HCV. (A) Strategy to identify candidate effectors of the IFN-γ response against HCV by gene expression analysis. Huh-7 and Huh6 cells were treated with 1,000 IU/ml of IFN-γ or left untreated for 24 h. Total RNA was used for gene expression analysis by Affymetrix HGU133A Plus 2.0 Genechip microarray. Relative induction by IFN-γ treatment was calculated for each cell line, and relative induction values in Huh-7 cells were divided by relative induction values in Huh6 cells for each gene. Genes with more than ca. 3-fold (log2 > 1.58) higher induction in Huh-7 cells were considered candidate effectors of IFN-γ. (B) Experimental strategy used for screening of candidates. siRNAs directed against candidate genes listed in Table 1 were transfected together with HCV FLuc reporter replicon RNA (genotype 1b or genotype 2a) into naive Huh-7-Lunet cells. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were treated with 0.15 ng/ml of IFN-γ. HCV replication was determined 96 h after transfection by luciferase assay. (C) Results of the primary candidate screening. The experiment was performed as described for panel B, using genotype 1b (LucCon1ET) reporter replicons. Luciferase activity was normalized to that of the untreated siNT control. siIFNgR was used as a control for rescue of HCV replication. The experiment was performed twice; shown are means with SDs. (D) siRNAs against DDX60L were tested in the same setting as for panel B, but using a genotype 2a FLuc reporter replicon (LucJFH1) instead. Luciferase values were normalized to that of the untreated siNT control. Experiment was performed twice; shown are means with SDs. Note that in the case of siDDX60L_5, results did not reach statistical significance due to high variability among independent replicates. (E) Knockdown efficiency of siRNAs against DDX60L in the presence and absence of IFN-γ. DDX60L mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR 48 h after transfection. Results were normalized to those for untreated siNT.