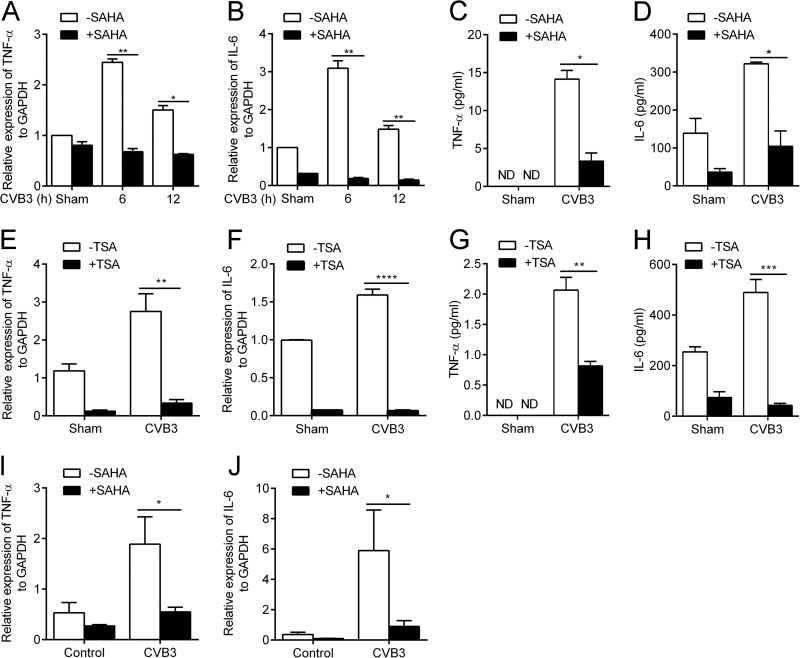
FIG 2.
HDACI significantly suppresses CVB3-induced proinflammatory cytokine production. (A and B) Cardiac myocytes were sham infected or infected with CVB3 for the indicated time points at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 5 in the presence or absence of 1 μM SAHA. Total RNA was extracted and subjected to real-time RT-PCR for TNF-α (A) and IL-6 (B) transcript level analysis (n = 3). (C and D) Cells were treated as described for panels A and B for 24 h. Levels of TNF-α (C) and IL-6 (D) in the cell culture supernatants were determined by ELISA (n = 3). (E and F) Cardiac myocytes were sham infected or infected with CVB3 for 12 h (MOI, 5) in the presence or absence of 1 μM TSA. Real-time RT-PCR was used for TNF-α (E) and IL-6 (F) transcript level analysis (n = 4). (G and H) Cells were treated as described for panels E and F for 24 h. Levels of TNF-α (G) and IL-6 (H) in the cell culture supernatants were determined by ELISA (n = 4). (I and J) BALB/c mice were sham infected with PBS (control) or infected with CVB3 on day 0 and then treated (or not) with SAHA (50 mg/kg) daily from day 0 to day 7 p.i. Total RNA was extracted from heart tissues of the mice on day 7 p.i. and subjected to real-time RT-PCR for TNF-α (I) and IL-6 (J) transcript level analysis (n = 6). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; ND, not detected.