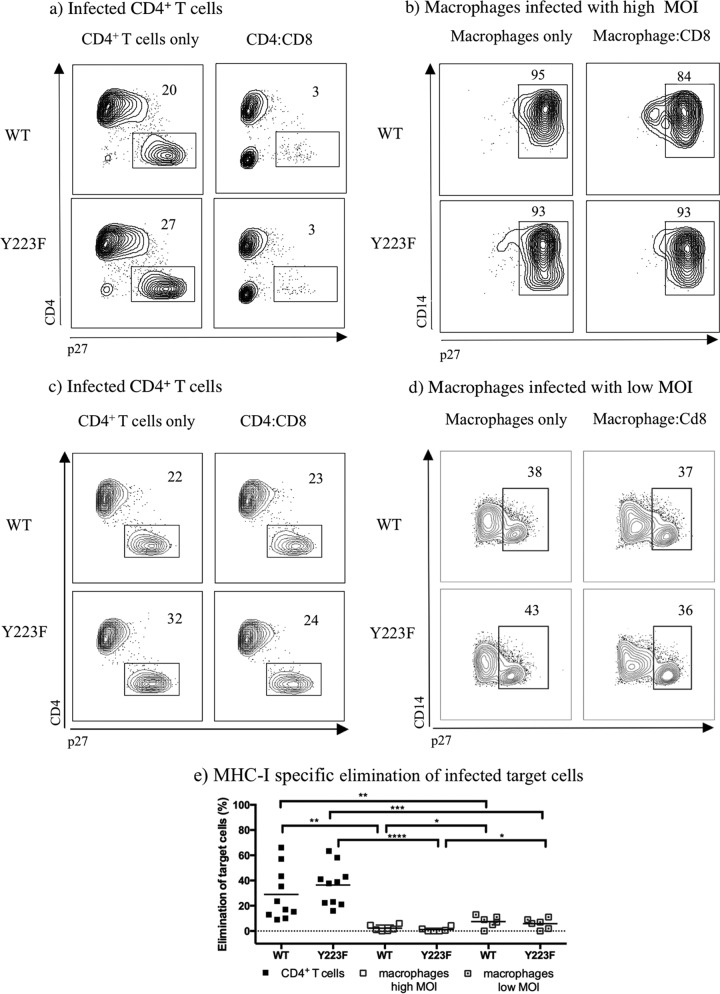
FIG 4.
Freshly sorted SIV-specific CD8+ T cells are more effective at eliminating CD4+ T cells than macrophages when infected with Y223F. (a to d) Contour plots representing intracellular p27 staining of MHC-I-matched target cells infected with WT- and Y223F virus as indicated. Contour plots were generated by gating on live CD8− T cells or live CD14+ macrophages from one representative experiment. (e) MHC-I-specific elimination in WT- and Y223F-infected target cells, including macrophages infected at a low MOI, after subtraction of MHC-I-mismatched nonspecific killing. The mean percent elimination of target cells is represented as a black line, and each data point represents an independent experiment. Cocultures of macrophages infected at a high MOI were performed with Gag181–189 CM9- and Nef137–146RL10-CD8+ T cells isolated from multiple elite controller animals. Cocultures with low MOI-infected macrophages included Gag181–189 CM9- and Vif66–73HW8-CD8+ T cells isolated from infected or vaccinated animals. Two experiments included Nef137–146RL10-CD8+ T cells from an elite controller as effector cells. P values: ****, <0.0001; ***, 0.0001 to 0.001; **, 0.001 to 0.01; *, 0.01 to 0.05.