Fig. 2.
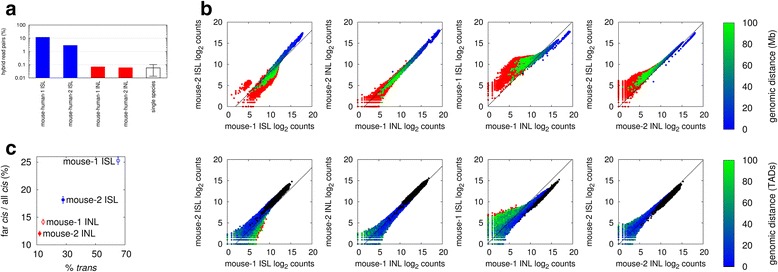
In-nucleus ligation reduces noise from Hi-C datasets. a The frequencies of hybrid mouse-human di-tags obtained from the mixture of mouse and human cells by in-solution (ISL; blue) and in-nucleus (INL; red) ligation experiments, compared with the mean hybrid di-tag frequencies in unmixed mouse or human samples (single species; white, with standard deviation). b Scatter plots comparing the log2 binned interaction counts for mouse datasets at 10 Mb resolution (top panels), and topologically associated domain (TAD) scale (bottom panels). Colors represent interaction distances according to the color bar shown; red dots represent trans-chromosomal interactions, black dots represent intra-TAD interactions in bottom panels. Dashed lines show the interaction counts corrected for the difference in the total counts. c The ratio of far-cis (>20 Mb) to all cis-chromosomal interaction counts plotted against the ratio of trans-chromosomal to all interaction counts (Pearson R > 0.98)
