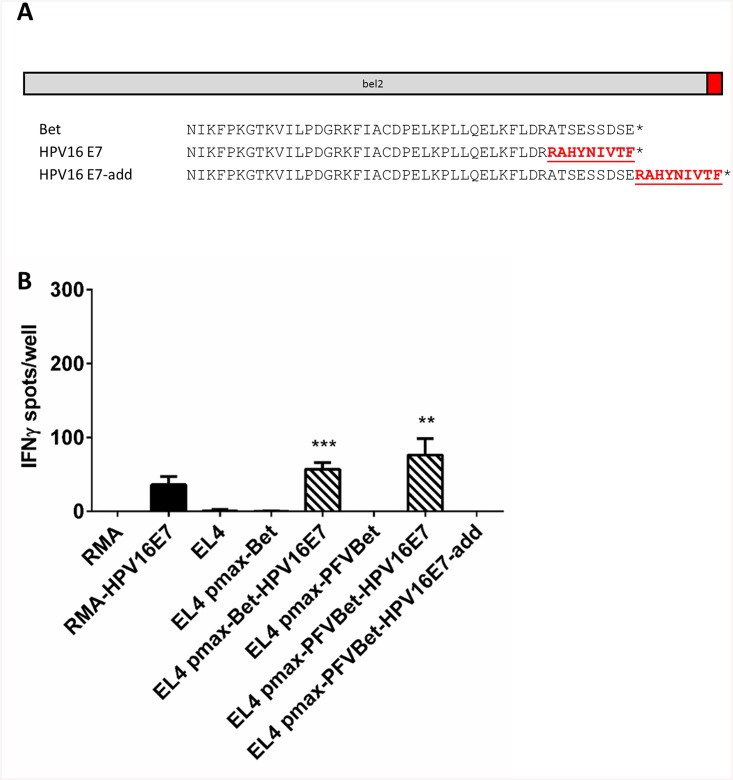
Fig 7. Recognition of the HPV16 E7-derived H2-Db-restricted epitope RAHYNIVTF incorporated into the PFV Bet C-terminus by E7-specific CTLs.
A) The coding sequence for PFV Bet was cloned into the expression vector pmaxGFP to yield pmaxPFVBet. The HPV16E7 T cell epitope RAHYNIVTF was cloned into the C-terminus of PFV Bet. A replacement of the last nine amino acids of PFV Bet resulted in pmaxPFVBet-HPV16E7. Upon addition of the nine amino acids to the C-terminus of PFV Bet pmaxPFVBet-HPV16E7-add was generated. Original protein sequences are shown in black and modifications are depicted in red. B) EL4 cells were nucleofected with pmaxPFVBet, pmaxPFVBet-HPV16E7, or pmaxPFVBet-HPV16E7-add. After 2 d, cells were harvested and analyzed in an IFNγ ELISpot assay using HPV16E7-specific CTLs. The HPV16 E7-expressing transfectant clone RMA-E7 and RMA cells transfected with the FFV Bet-encoding plasmid pmax-Bet-HPV16E7 were used as positive control. Untransfected EL4 cells and EL4 transfected with FFV and PFV pmaxBet vectors were used as negative controls. Results are shown as number of IFNγ spots per 1250 CTLs/well. Values represent a single experiment performed in triplicate. ** represents a p-value of less than 0.01 when compared to pmaxPFVBet; ***, p-value < 0.001.