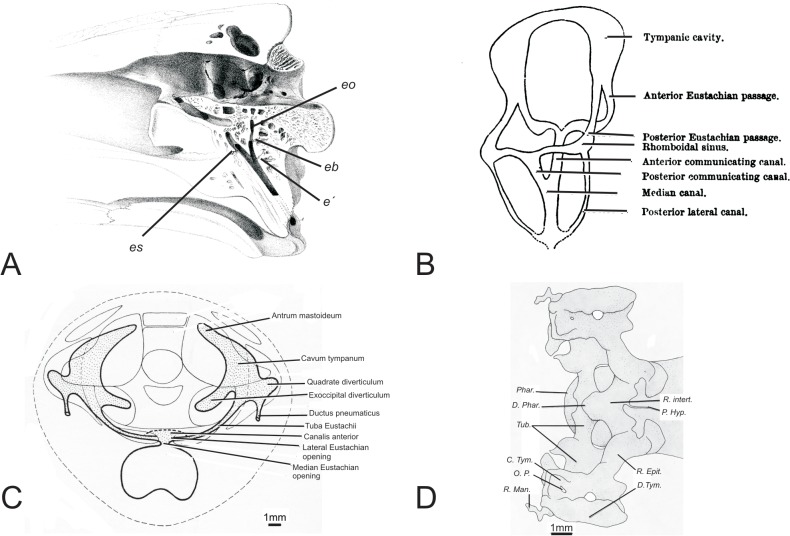
Fig 2. Previous representations of the crocodilian middle-ear space shown as A) a lithographic rendering of a parasagittal cut through the skull of a crocodile, adapted from Owen, 1850; B) a schematic depiction of the communicating canals of the tympanic cavity in rostral oblique view, adapted from Miall, 1878; C) a schematic showing the development of the tympanic cavity in a late stage embryo of Crocodilus cataphractus in rostrocaudal aspect, adapted from Müller, 1967; D) A schematic of the development of the tympanic cavity in a late stage embryo of Alligator mississippiensis in dorsal view, adapted from Simonetta, 1956.
C. Tym., Tympanic cavity; D. Phar., Posterior pharyngeal diverticulum; D. Tym., Tympanic diverticulum; e’, bifurcation of the median Eustachian canal; eb, bifurcation of the basioccipital branch, eo, basioccipital branch of the Eustachian canal; es, basisphenoidal branch of the Eustachian canal; O.P., paratympanic organ; Phar., Pharynx; P. Hyp., Hypophyseal pedicle; R. Epit., epitubaric recess; R. Intert., intertympanic recess; R. Man., mandibular recess; Tub., Eustachian tube.