Fig. 2.
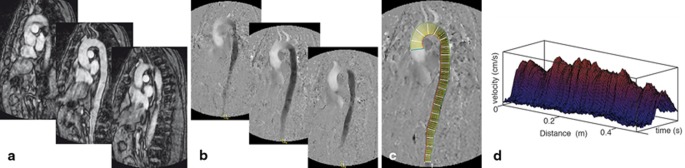
Representation of image acquisition and analysis of regional PWV in a TAA patient. Regional PWV was assessed by means of combining two consecutive acquisitions of a stack of three consecutive slices (a), both with one-directional velocity-encoding in anterior-posterior and feet-head direction (b), respectively. The stack of three slices covered the entire aorta. Using MASS MRI software, 200 equidistantly-spaced sampling chords were defined (c). At each sampling chord, the maximal velocity along the aortic centreline was determined for each cardiac phase, resulting in 200 velocity-time waveforms (d). From the corresponding measurement position (distance (x)) along the aortic centreline and time of arrival of the pulse wave (arrival time (t)) at each position, the local aortic pulse wave velocity was determined. PWV pulse wave velocity, TAA thoracic aortic aneurysm, VE velocity-encoded, MRI magnetic resonance imaging
