Figure 3.
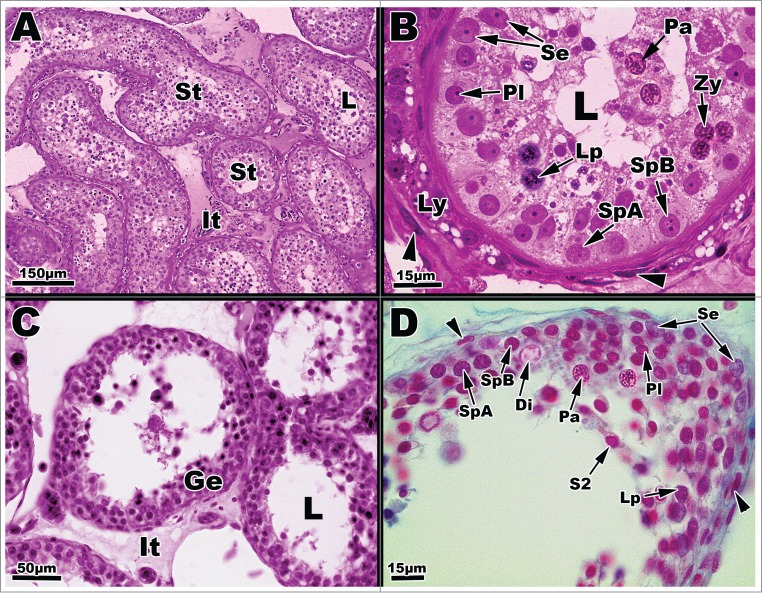
Light micrographs of seminiferous tubules of Graptemys pseudogeographica kohnii from in June (A–B) and July (C–D). (A) Seminiferous tubules (St) surrounded by interstitial cells (It); L = lumen. (B) A cross section of June seminiferous tubule reveals several cell types, including a type A spermatogonium (SpA), type B spermatogonium (SpB), pre-leptotene spermatocyte (Pl), leptotene spermatocyte (Lp), zygotene spermatocyte (Zy), pachytene spermatocyte (Pa), and Sertoli cells (Se); Leydig cells (Ly) are mostly void of lipid. Arrow points to a fibroblast nucleus; L = lumen. (C) July Seminiferous tubules lined with seminiferous epithelia (Ge) surrounded by the interstitium (It); L = lumen. (D) July seminiferous tubule exhibiting a variety of germ cell types including type A spermatogonium (SpA), type B spermatogonium (SpB), pre-leptotene spermatocyte (Pl), leptotene spermatocyte (Lp), pachytene spermatocyte (Pa), diplotene spermatocyte (Di), Sertoli cells (Se), and a step 2 spermatid (S2). Arrowheads point the nucleus of fibroblast cells. Paraffin, (C-D); plastic (A-B).
