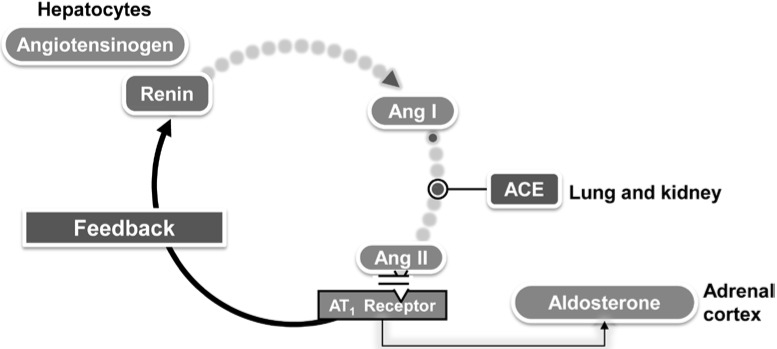
Figure 6.
Schematic of the classic RAAS system cascade. The biosynthesis of renin by the juxtaglomerular cells is a key determinant of the activity of the RAS. Renin regulates the initial, rate-limiting step of the RAS by cleaving the N-terminal portion of a large molecular weight globulin, angiotensinogen, to form the biologically inert decapeptide Angiotensin I or Angiotensin-(1–10). The inactive decapeptide Angiotensin I is hydrolyzed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which removes the C-terminal dipeptide to form the octapeptide Angiotensin II [Ang-(1–8)], a biologically active, potent vasoconstrictor.