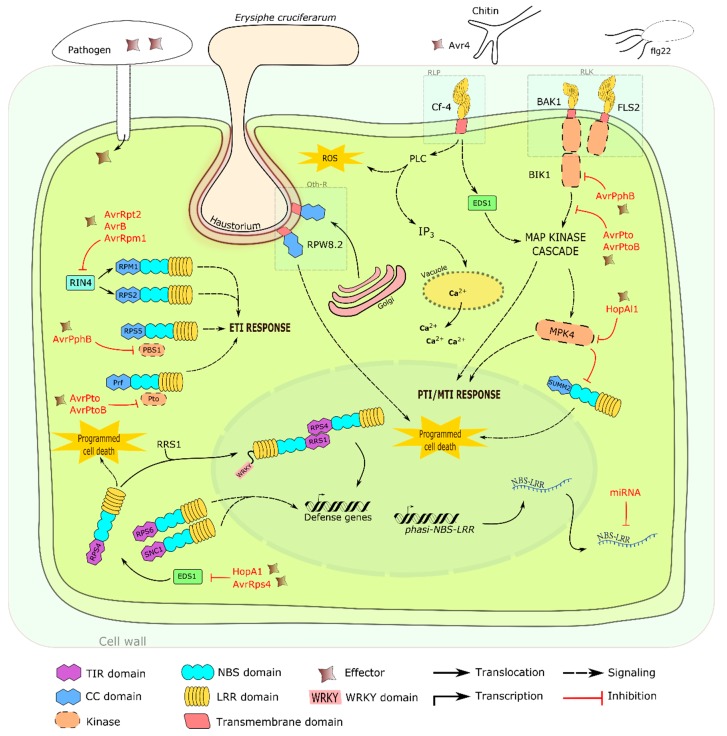
Figure 2.
Intracellular signaling mechanisms of RGAs in plant defense. RIN4, PBS1, Pto and EDS1 are targeted and modified by numerous effectors and, as a result, their corresponding TNL or CNL will detect the modification to initiate ETI responses [162,163,164]. TIR-TIR interactions occur between RPS4 and RRS1 to further activate defense genes [169]. Flg22, a bacterial PAMP, activates FLS2 and BAK1 RLKs to initiate the MAP kinase cascade that triggers PTI/MTI responses [170]. MAP kinase cascade signaling can be interrupted by pathogenic effectors. When MPK4 is compromised, SUMM2 will not be inactivated and will initiate PCD [165]. Effector Avr4 is recognized by Cf-4 RLP to initiate MAP kinase cascade and ROS production while simultaneously increasing calcium levels in the cytosol [171]. Upon Erysiphe cruciferarum infection, RPW8.2 can translocate from the Golgi to the extrahaustorial membrane where the fungal haustorium has penetrated to activate the downstream signaling of PCD [172,173]. Under normal conditions, NBS-LRR transcripts derived from the PHAS locus are regulated through transcript degradation by miRNAs [174]. Such miRNAs include, among others, miR1510, miR1507, miR2109, miR482/2118, miR5668, miR5376, miR172 and miR5041 [174,175,176]. Single arrows may indicate multi-step processes.