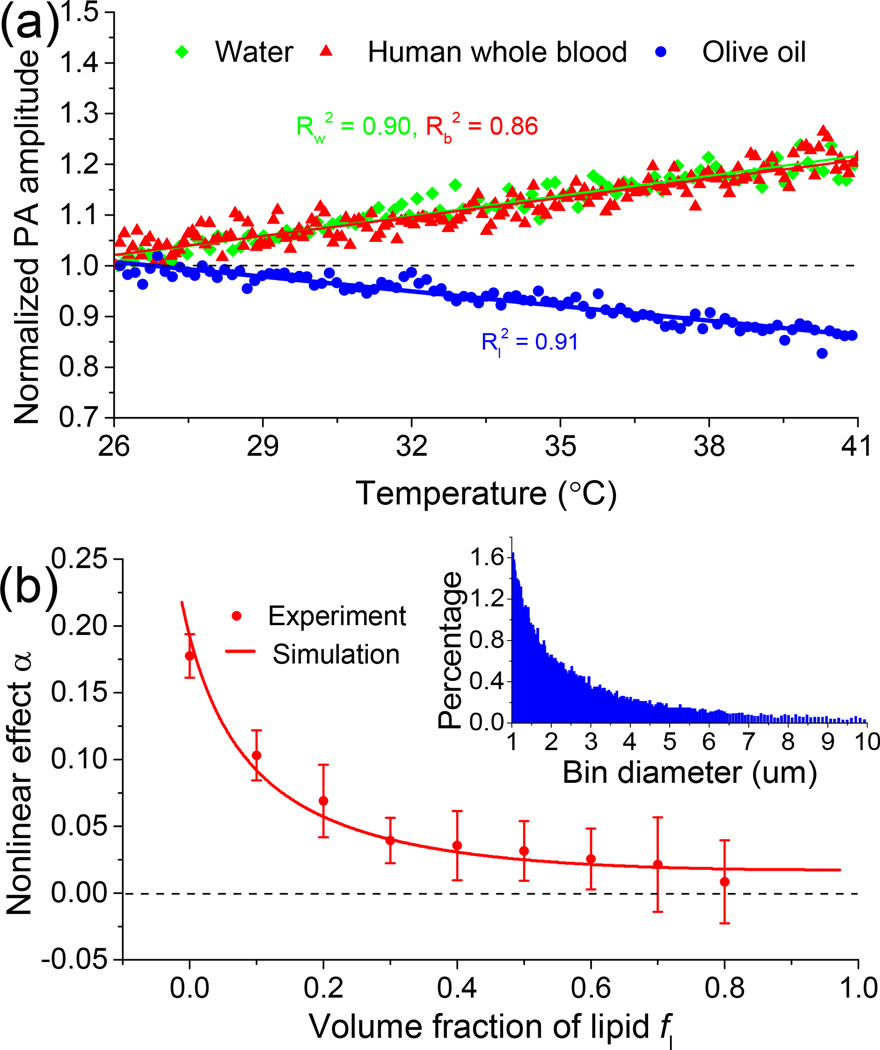
Fig. 2.
(a) Photoacoustic signal amplitude as a function of temperature for water, human whole blood and olive oil. (b) Dual-pulse nonlinear photoacoustic effects of samples of blood and lipid mixtures with different lipid volume fractions. The inset shows the probability distribution of oil and water droplets with size.