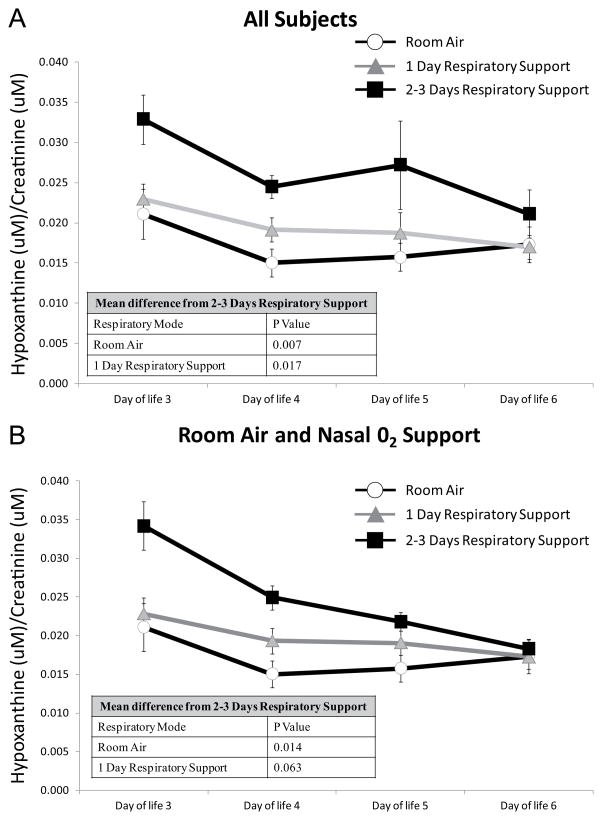
Figure 3.
Effect of Number of Days of Respiratory Support on Urinary Hypoxanthine in Infants Diagnosed as Poor Nippling Plus Early Respiratory Disease.
(A) Infants on room air, receiving nasal oxygen support (high flow nasal cannula, nasal continuous positive airway pressure, or nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation) or synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation. (B) Infants on room air or receiving nasal oxygen support (high flow nasal cannula, nasal continuous positive airway pressure, or nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation) only. P values represent significant differences between the indicated group and infants on 2 to 3 days respiratory support over time.