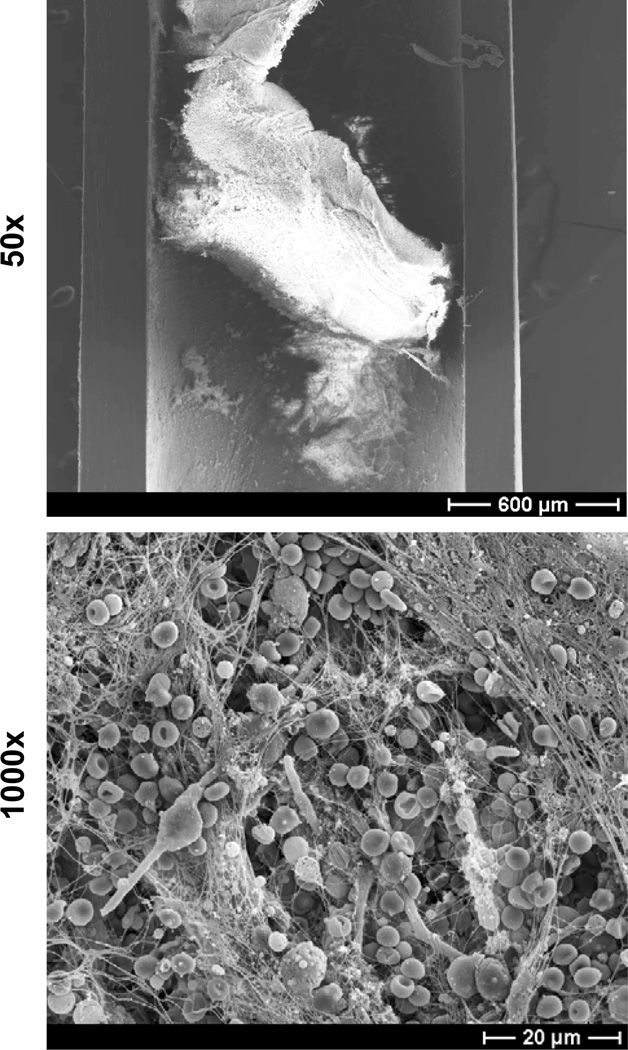
Figure 3. C. albicans biofilm infection of rat jugular venous catheter.
C. albicans was instilled in the lumen of a subcutaneously tunneled jugular venous catheter and allowed to dwell for 6 hours. After a growth period of 24 hours, the catheter was harvested, fixed, and dehydrated. Catheter segments were imaged by scanning electron microscopy on a JEOL JSM-6100 at 10 kV (50× and 1000×). The biofilm is composed of both yeast and hyphae encased in an extracellular matrix. Host components, including red blood cells, appear to associate with the biofilm.