Figure 6.
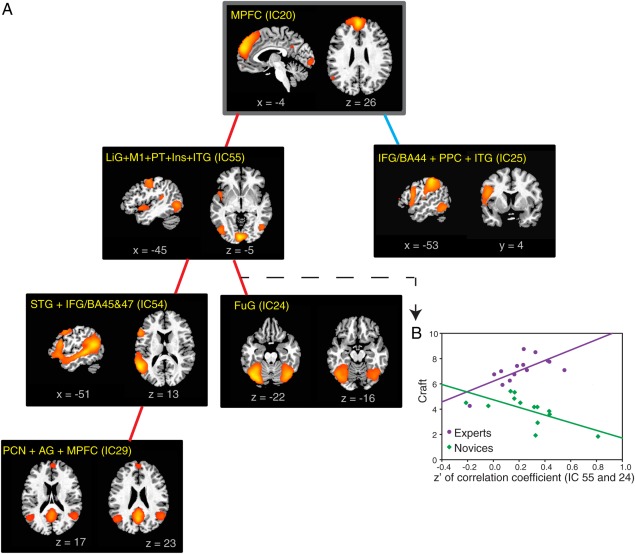
Distinct associations between craft ratings and connectivity patterns in experts and novices.
(A) An analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model was used to examine group differences in the way craft scores were correlated with functional connections in experts and novices. In experts, craft scores were more tightly correlated with the strength of connections from the MPFC to a set of ICs including perisylvian areas, fusiform and angular gyri, precuneus and a mixture of motor and sensory areas, in a cascading fashion (indicated by red lines, see an example in Fig. 6B). On the other hand, in experts craft scores were more weakly correlated with the strength of connection between the MPFC and a component containing the dorsal portions of the IFG (BA44) and posterior parietal areas than they were in novices (indicated by the blue line) (FDR < 0.05 in each instance). (B) The relationship between ICs 55 and 24 is used to illustrate an instance in which craft score and functional connections were more strongly correlated in experts than in novices. The correlation (slope of the linear fit) between craft score and Fisher's z’ transformed correlation coefficient (of IC 55 and 24) is significantly greater (P = 0.0002, FDR = 0.008) in experts (purple: y = 6.21 × x + 4.10, P = 0.005) than in novices (green: y = −3.02 × x + 4.74, P = 0.01). AG, angular gyrus; FuG, fusiform gyrus; Ins, Insula; ITG, inferior temporal gyrus; LiG, lingual gyrus; M1, primary motor cortex; PCN, precuneus; PPC, posterior parietal cortex; PT, planum temporale; STG, superior temporal gyrus.
